
The National Ocean Industries Association (NOIA) report, The NOIA ESG Network 2024 Report of the Offshore Energy Industry: Managing Emissions and Developing the Workforce of Tomorrow, highlights the work done by the NOIA Environmental, Social & Governance (ESG) Network and NOIA members to share and develop the best ESG practices across the offshore energy industry, including eleven case studies in emissions reduction or diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) programs.
NOIA President Erik Milito said, “The NOIA ESG Network and our fourth annual ESG report underscore the innovation and commitment companies apply towards building the workforce of tomorrow and tangible progress in emissions reduction efforts -- two key and critical areas of importance for the industry in the ESG paradigm. Our industry is driven by visionary leaders and innovators who recognize their pivotal role in advancing societal progress. Whether it's delivering dependable, cost-effective, and environmentally responsible energy or fostering workforce development opportunities from the field to the boardroom, NOIA members contribute to a remarkable ecosystem that enhances the world. While there continue to be complexities and uncertainties within the field of ESG, the offshore sector continues to perform at the highest levels in environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and corporate governance.”
Paul Danos, NOIA Chairman and Owner & CEO of Danos, said, “Improving our environmental performance, progressing society forward, and being the ‘best neighbor we can be’ have long been a fundamental part of how the offshore energy industry does business. Our industry is a network of thousands of companies and hundreds of thousands of workers who want to safely and sustainably support and promote the betterment of local communities. The variety of companies participating in this year’s report underscores how deep and serious our industry takes ESG performance.”
NOIA ESG Network 2024 Report At-A-Glance:
- The report features case studies in emissions reduction from NOIA member companies:
- NOIA released a comprehensive study on global oil production emissions completed by ICF International, the GHG Emission Intensity of Crude Oil and Condensate Production. The report reveals that the greenhouse gas intensity of U.S. oil production, particularly in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico, is significantly lower compared to most other regions around the world.
- NOIA hosted several in-person events on ESG topics, including: The Workforce of the Future; Improving DEI in the Workplace and Fostering an Inclusive Work Environment; Unconscious Bias; Building Support for Offshore Wind; The Investment Outlook for Offshore Wind; and Policy Considerations for U.S. Offshore Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
- NOIA and the Offshore Operators Committee hosted the Offshore Carbon Capture and Storage Symposium at Rice University’s Baker Institute. The symposium included sessions on Successful Global CCS Projects; The Role of Inflation Reduction Act Tax Credits in Accelerating Investment; Louisiana’s CCS Leadership; Current Technologies to Springboard CCS
- The 2023 NOIA ESG Workshop tackled key issues, including: Technology Advances Improve Emissions Management; The Value of Conscious Leadership in Realizing ESG objectives; and ESG, Insurers, and Why the Oil and Gas Industry Needs to Lead the Conversation
- NOIA named TechnipFMC as the winner of the second annual NOIA Environmental, Social, & Governance (ESG) Excellence Award.
- Halliburton and Oil States International presented to NOIA membership on their award-winning NOIA Safety in Seas entries.
- NOIA is continues to advocate for legislation such as the Reinvesting in Shoreline Economies & Ecosystems (RISEE) Act and The Offshore Wind Jobs and Opportunity Act as well as commenting on The Renewable Energy Modernization Rule will other groups.
To learn about the NOIA ESG Network, read the NOIA ESG Network Foundational, Environmental, Social & Governance Principles and see the list of companies who have signed the NOIA ESG Network Participation Agreement click here.
 In its ongoing efforts to reduce emissions, Beacon Offshore Energy LLC, (“Beacon”) continues to emphasize leveraging the latest technologies in its rig and marine vessel operations. Beacon’s efforts are centered around four key elements: OSV Fleeting Strategy, Enhanced Electronic Fuel Management Systems, Dynamic Positioning (DP) Operating Philosophies, and Diesel Fuel with Enhancing Additives.
In its ongoing efforts to reduce emissions, Beacon Offshore Energy LLC, (“Beacon”) continues to emphasize leveraging the latest technologies in its rig and marine vessel operations. Beacon’s efforts are centered around four key elements: OSV Fleeting Strategy, Enhanced Electronic Fuel Management Systems, Dynamic Positioning (DP) Operating Philosophies, and Diesel Fuel with Enhancing Additives.
OSV Fleeting Strategy
The Beacon fleeting strategy emphasizes employing vessels with diesel-electric propulsion systems which allow for variable RPM versus fixed RPM operations. In certain operational configurations, variable RRM operations achieve up to a 50% fuel burn efficiency. Across the vessel’s operational spectrum, total reduction of fuel burn has averaged ten percent. At an individual vessel level this can reduce CO2 by 207,487 kg which is equivalent to 45 passenger cars or 2,305 cruising hours on a 737 annually.
Diesel-electric variable speed engines offer an innovative approach in the pursuit of reducing CO2 emissions. Diesel-electric variable speed engines integrate the diesel generators with electric propulsion systems and operate by generating electricity through diesel engines, which then powers electric motors to drive the machinery.
Unlike traditional fixed-speed diesel engines, these systems allow for variable speed operations. By modulating the engine speed to meet the instantaneous power needs of the vessel, engines can run closer to their peak efficiency, minimizing fuel consumption, and subsequently reducing CO2 emissions. Furthermore, diesel-electric systems enable the use of energy regeneration techniques. When the load decreases, excess energy can be redirected to charge batteries or other energy storage systems, reducing waste and further enhancing efficiency. This stored energy can then be utilized during peak demands, lowering the reliance on diesel consumption. While Beacon does not currently have vessels outfitted with energy storage systems such as batteries, as this technology expands to the OSV markets, it will be a consideration in the Beacon fleeting strategy.
Enhanced Electronic Fuel Management Systems
To complement diesel-electric propulsion systems, Beacon is investing in the installation of new advanced electronic fuel management systems on its term Offshore Supply Vessels (OSVs). These advanced fuel management systems are designed to help vessel operators increase efficiency and reduce both fuel burn and emissions by optimizing speed versus economy. Advanced fuel management systems employ independent precision sensors that deliver auditable ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) data to decision-makers in real-time. Throttle optimization protocols are available to onboard personnel, and shoreside users can configure alerts for deviations from best practices.
Dynamic Positioning Operating Philosophies
Using the latest technology, power management systems on rigs and vessels allow for the connection between the two switchboards into one (Closed Bus) with a "smart" circuit breaker. This circuit breaker recognizes potential electrical failures in such a short time (nanoseconds) that it will automatically open and separate the power (open the bus) before the fault has a chance to affect the entire system. Closed Bus operations reduce the number of generators/engines required online. By taking advantage of this technology, Beacon can maintain safe operations while reducing power consumption and emissions.
Diesel Fuel with Enhancing Additives
Beacon continues to support its previous investment in upgrades to allow drillships to automatically dose fuel additives during drilling and completion operations. Proprietary fuel additives are designed for diesel engines. It raises the ignition quality of the fuel, allowing ignition at lower compression and a longer burn during each stroke. This improves combustion and lowers the amount of unburned fuel expelled in the exhaust. The use of the fuel additive also reduces the heat of combustion, lowering nitrous oxide (NOx) emissions. Due to more efficient fuel use, Beacon is experiencing between 4% and 6% less fuel, with less CO2E produced, providing an annual reduction of more than 2400 MT CO2E in carbon dioxide equivalents and an annual fuel cost savings of more than $500,000.
In summary, on an annualized basis Beacon estimates that the combined results from its multifaceted GHG reduction strategies will reduce CO2 emissions by 3,700 metric tons. Commensurate savings of approximately 360,000 gallons of diesel fuel and an estimated dollar saving approaching $1 million based on current fuel prices.
Learn more about Beacon Offshore Energy here.
 Workforce Development – Danos’ On-the-Job Learning Program
Workforce Development – Danos’ On-the-Job Learning Program
The need to find and train new workers is an ongoing concern within the energy industry. As more experienced personnel retire from the workforce, it is imperative that a new generation of workers is prepared to step up and replace the vacancies. Danos is advancing workforce development and diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) through our on-the-job learning program, also known as the internship program.
Danos’ on-the-job-learning program partners with community and technical colleges and with our customers. It has two major aims: first, to provide a solution for the industry talent gap with a more inclusive and diverse workforce. And second, to ensure students receive job-relevant training and opportunities with hands-on skill development.
This innovative program offers students and recent graduates who are interested in energy careers the opportunity to gain valuable experience at real job sites. By intentionally promoting the program to students of varied backgrounds and demographics, and by providing practical experience, Danos is contributing to the growth of diverse new talent for the industry.
Each participant in the program spends six to nine months receiving hands-on training in an offshore or onshore environment. Internship opportunities are made possible through the support of oil and gas operators - Danos customers.
Since the program began in 2018, Danos has placed 89 employees. 71 of the 89 individuals have been hired for internship rolls. The other 18 were hired for entry level roles from the candidate pool through program partners. 21 of the 89 hires are females, and 50 are from a diverse background based on gender, race, or veteran status.
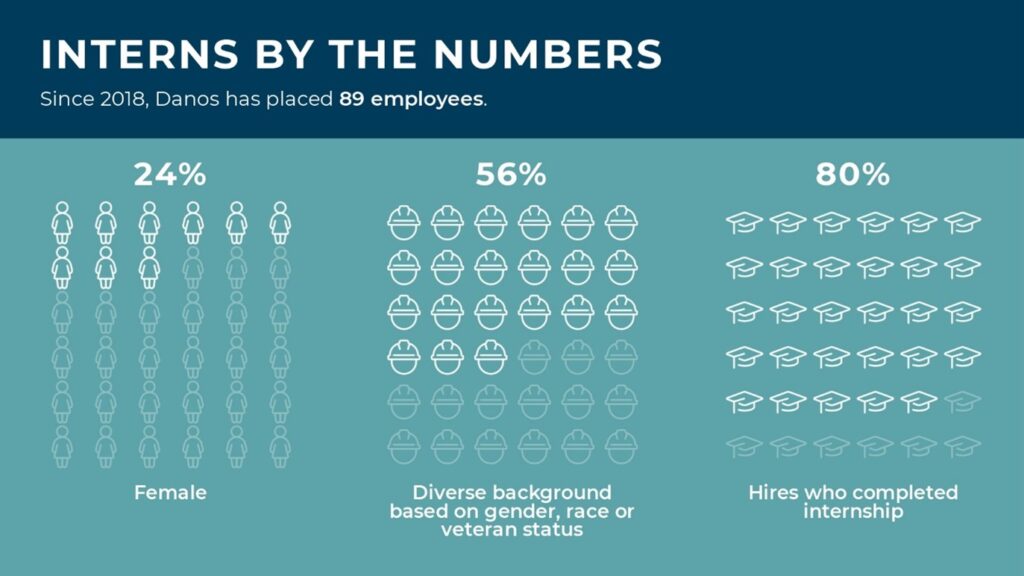
In addition to the program's benefits for students, it also serves the needs of oil and gas businesses and the industry. Danos currently partners with 16 technical and community colleges throughout Louisiana, Mississippi, Texas and Alabama. The program has led to improved curricula and the development of a more competent and diverse applicant pool available to address the needs of operators and producers. It has also generated greater enthusiasm and awareness of the benefits of oil and gas careers. These advances help to strengthen the pipeline of talent needed to power the industry into the future.
Danos is a family-owned company, driven by values, vision and purpose. It’s something that sets the company apart, guiding its actions in everything from high-level strategy to day-to-day worker interactions. Its core purpose is honoring God and developing great people to solve big challenges for customers and communities. This on-the-job-learning program reflects Danos’ vision to set the standard for operational excellence, customer service and care for people. Through the support of customers and collaboration with participating schools, Danos is developing the next generation of workforce - one intern at a time.
Emissions Reduction Through Releasable Mooring System
Delmar Systems is helping its customers reduce their carbon footprint and costs by utilizing its revolutionary RAR Plus™ Releasable Mooring System. This system consists of Delmar’s proven and industry preferred RAR Plus™ tool, Seafloor Safe fiber, and Delmar’s patented StevsharkREX® anchors.
The RAR Plus is a patented, fully redundant, and quick‐release tool that allows for rapid release or mooring lines under tension using acoustic triggering technology with a mechanical backup. The backup mechanical release bypasses the acoustic, electric, and hydraulic systems in the RAR Plus, and can be actuated from the rig itself, ensuring that the tool releases 100% of the time without the need for an Anchor Handling Tug Supply (AHTS) vessel or ROV assistance.
The RAR Plus has been used by a wide client base and has been deployed all over the world. It has a proven track record of success, with over 45,000 connected days and over 700 mooring line releases without a single failure, allowing customers to unmoor their assets with confidence – in less than one hour.
The figure below shows the fuel savings and CO2 emission reductions that can be achieved by comparing a DP/Moored rig operating on a traditional preset mooring system with and without the RAR Plus™ Releasable Mooring System. These savings are achieved through eliminating the need for AHTS vessels, MODU critical path time , and associated fuel and CO2e reductions during MODU mooring disconnection. It should be noted that increased downtime due to weather and operational delays, or longer mobilization or vessel transit times, will often increase these fuel and emission savings substantially.
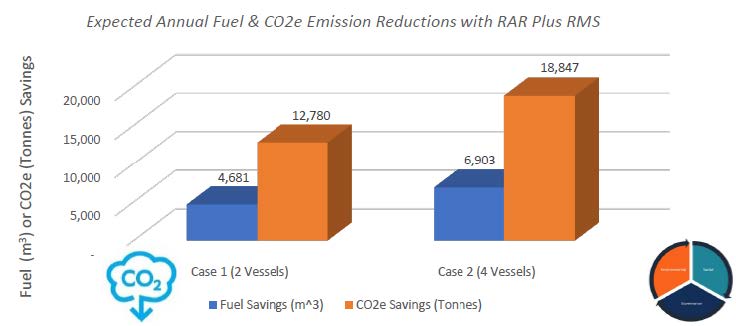 Besides CO2 emissions reduction, other benefits of the RAR Plus™ Releasable Mooring System include cyclone/hurricane evasion, iceberg evasion, reduced HSE exposure, rig move efficiency and cost savings.
Besides CO2 emissions reduction, other benefits of the RAR Plus™ Releasable Mooring System include cyclone/hurricane evasion, iceberg evasion, reduced HSE exposure, rig move efficiency and cost savings.
Emissions (and Noise) Reduction of Mooring vs DP
Mooring of an offshore asset, such as a semi‐submersible rig or a drillship, is a green alternative for dynamic positioning (DP) if the drilling project is expected to last beyond 15 days, or 10 days if the RAR Plus is used. An asset operating on DP maintains its position using thrusters, which is a continuous source of fuel consumption that generates substantial CO2 emissions. However, mooring eliminates the need for operating thrusters and therefore eliminates the associated CO2 emissions. The graphs below show the breakeven point in well duration (days) after which point moorings result in significant emissions reduction, with or without the RAR Plus.
Additionally, the use of moorings on an asset instead of DP substantially reduces acoustic emissions, which is beneficial for marine life. In fact, Australia’s National Offshore Petroleum Safety and Environmental Management Authority (NOPSEMA) has rejected DP permits due to acoustic emissions and the negative impacts on marine fauna. According to NOPSEMA, “marine fauna impacts that may be attributed to acoustic emissions in the marine environment include mortality, physical injury, hearing loss (permanent or temporary), stress, diminished health, masking of communication, displacement from important habits and behavioural disturbance.” Additional indirect impacts identified by NOPSEMA include “prey displacement or depletion, reduced catchability or stock availability of commercially targeted fish species, and reduced reproductive success.”
Using releasable mooring systems instead of DP has the potential to play a critical part in offshore operators achieving their carbon emissions reduction goals and protecting marine life.
 Emissions Reduction at Halliburton: Adding value to customers
Emissions Reduction at Halliburton: Adding value to customers
In 2020, Halliburton recognized deficiencies in existing solutions to standardize emissions governance, integrate emissions into existing systems, and provide consistent decision-making emissions information to customers. Recognizing this as an industry-wide need, Halliburton's Sustainability team initiated a transformative journey.
Solution:
Envana meets the oil and gas industry's need for a tailored emissions management solution. Envana innovation and product development stemmed from Halliburton’s 100+ years of experience and understanding of the oil and gas market. Tailored to address the unique needs of the oil and gas industry, Envana Catalyst emerged as a comprehensive emissions management solution. Leveraging a bottom-up approach to calculations and emissions inventory, the software became the cornerstone of Halliburton's emissions management strategy to decarbonize core operations and empower clients with actionable data.
Envana Catalyst allows Halliburton business lines to use the most up to date models for job-level emissions estimation. Envana Catalyst seamlessly integrates with multiple resource and operations planning software, facilitating the identification of lower-carbon options within budget constraints, and embedding emissions impact into project planning and operations.
At Halliburton, Envana Catalyst has been integrated into service delivery workflows that cover about 75% of Halliburton’s Scope 1 and 2 emissions. This reduces the burden on operations and allows for complete, consistent and correct emissions calculations. Halliburton continues to implement Envana Catalyst throughout the rest of the business lines that generate Scope 1 and 2 emissions, enabling the company to provide repeatable and auditable reporting—based on consistent methodology and clear activity-based methods— where implemented.
Result:
Integration of Envana into service delivery workflows of select Halliburton Business lines has enabled the teams to generate actionable recommendations for emissions improvement throughout the asset lifecycle. This integration into standard workflows used for job planning and KPI collection allows engineers to see the emissions impact of their choices while planning and after executing a project.
The benefits realized include efficiency gains, reduced manual data entry, and improved consistency in emissions governance. While the full potential of the software is yet to be realized, Halliburton's transition from one-off emissions calculations to a central hub with Envana Catalyst has provided consistency in governance of inputs, emissions calculations, and generation of outputs.
Conclusion:
Envana provides automatic emissions calculation that allows for traceability of data, consistency of calculation across the global organization and centralizes governance. It has enabled the user to become more efficient by reducing manual emissions calculations. Envana has simplified our emissions inventory process and allows us to meet our customer’s decarbonization objectives.

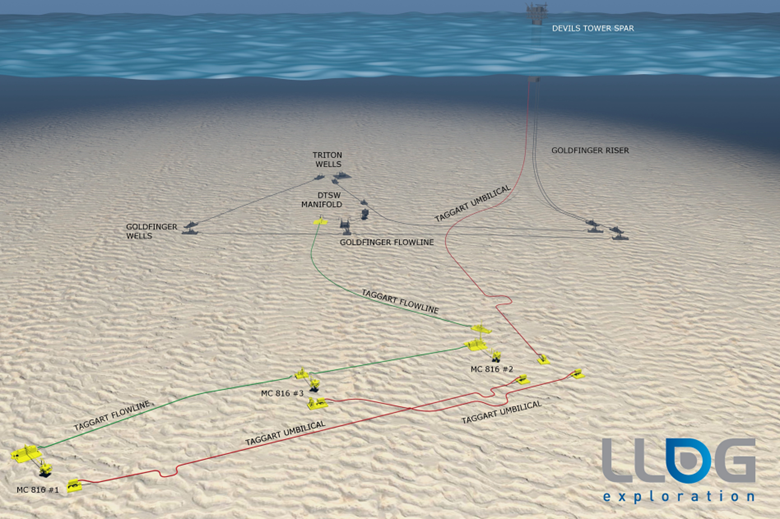
LLOG’s commitment to protecting and preserving the environment can be seen in a culture which is built around exceptional safety practices and minimizing their operational footprint. One example is the Taggart Field, a three-well development located in the Deep Water Gulf of Mexico, approximately 150 miles SE of New Orleans, LA and within a few miles of the Devils Tower Spar in Mississippi Canyon. While subsea tiebacks to third party platforms are fairly common, there was a unique opportunity to access an existing subsea manifold, flowline, riser, and topsides processing equipment that would bring the Taggart field online at a lower cost and with significantly lower greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions relative to a home run tieback to the Spar.
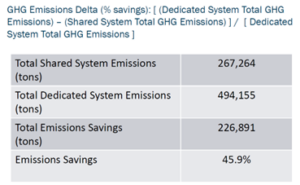
LLOG’s efforts to protect and minimize its operational impact on the environment is part of the evaluation of all of its projects. As a result, LLOG hired EDG Consulting Engineers to evaluate the emissions intensity of the proposed development plan, which resulted in emission savings of 46% due to the reduced scope of the project and the re-use of existing and under-utilized infrastructure.
 To make this subsea-to-subsea development plan into a reality, LLOG partnered with the infrastructure owners, none of whom had ownership in the Taggart discovery, to gain access to the manifold and the FPS. The deals created value for all stakeholders, while increasing production at a significantly lower carbon footprint and better utilizing existing infrastructure.
To make this subsea-to-subsea development plan into a reality, LLOG partnered with the infrastructure owners, none of whom had ownership in the Taggart discovery, to gain access to the manifold and the FPS. The deals created value for all stakeholders, while increasing production at a significantly lower carbon footprint and better utilizing existing infrastructure.
Prior to executing the commercial access agreements, LLOG and the infrastructure operator carried out multiple inspections to ensure that the integrity of the system was suitable to handle the new wells. Once completed, the parties signed a connection agreement to allow the Taggart satellite flowline to tie directly into the existing subsea manifold and ultimately back to Devils Tower for processing and export. Additionally, the production riser was equipped with gas lift which is critical for maximizing the expected oil recoveries from Taggart’s relatively shallow, low-pressure reservoirs.
 Using equipment-level energy data insights to drive sustainable behavior
Using equipment-level energy data insights to drive sustainable behavior
Noble has rolled out a fuel consumption monitoring solution fleetwide to support energy-efficient operations. During 2023, Noble completed the implementation of Energy Efficiency In-sights (EEI) on all its marketed rigs, which means the solution is now enabled on 29 rigs in total.
EEI is an emission-monitoring solution that supports the rigs in tracking, analyzing, and modeling emissions from operations, thereby allowing the crew to gain insights into potential emission reductions.
The EEI solution is proprietary and was developed in-house. By installing a multitude of sensors onboard a rig, fuel consumption and derived emissions can be monitored and tracked back to different energy consumers and types of operations. This can provide the basis for further modeling and identification of best practices. Lessons learned on emission reductions can then be shared between comparable rigs, contributing to smart behavior across the fleet.
Regular use of the system enhances awareness by providing real-time insights into energy usage, encouraging sustainable fuel consumption patterns onboard. The tool enables the optimization of daily activities and understanding the impact various energy efficiency initiatives will have on greenhouse gas emissions. It gives our operations transparency into fuel consumption and the impact of decarbonization efforts and enables customer dialog for collaboration. In this way, EEI establishes an important foundation for future initiatives in addition to the immediate impact from insights into potential improvements
The ability to see equipment-level consumption data on a rig paves way for catered sustainable behavior programs to further the rig’s dedication to reducing emissions. Noble aims to roll out a sustainable behavior program for rigs equipped with EEI to ensure the data collected builds stronger sustainability awareness and contributes to fuel and emission effi-ciency improvements.
The program also focuses on facilitating analysis and dialogue to identify best practices, including meeting with customers focused on consumption reduction and optimization of multiple aspects of daily operations, ranging from drilling equipment utilization to the temperature provided in accommodation. By facilitating this ongoing dialogue, the energy efficiency focus, and mindset become embedded onboard, so sustainable behavior remains top-of-mind for the crews and eventually becomes a habit.
Across multiple operations and rig types, it has been documented that EEI, supported by the sustainable behavior program, can deliver 6–10 percent reductions in fuel consumption and derived emissions.
“EEI is a game changer that we use actively to track our energy consumption patterns and overall environmental footprint. We host a bi-weekly ‘green meeting’ with our customer and EEI forms the base for discussions that have resulted in optimizing fan settings, thruster operations, drilling equipment utilization and reduced accommodation temperature amongst others.” — Jorgen Schaffer Rig Manager, Noble Venture
Ambition of diverse slate for onshore leadership positions
Embedded in Noble’s DEI policy is an ambition to include at least one individual on the slate of final candidates for senior onshore leadership positions who is diverse relative to the team by either gender, age, nationality, ethnicity and / or education. Since we commenced tracking slate diversity in August 2023, a female candidate has been included in the final slate in more than 60 percent of the cases, and a minimum of one candidate diverse relative to the team was observed in close to 90 percent of the cases.
During 2023, female representation in Noble’s onshore workforce has increased to 37 percent. Additionally, female representation in onshore leadership roles has increased to almost 30 percent.
Gender representation continues to be a challenge across the offshore oil and gas industry. Therefore, one of Noble’s DEI focuses is to promote equal employment opportunities and attract a gender diverse offshore talent pool.
In 2023, Noble embedded questions on the DEI experience for employees across our global workforce into a global employee engagement survey. This feedback loop is a critical element of Noble’s DEI roadmap and will help guide future efforts in the right direction.
“Being a workplace that keeps people safe, offers meaningful career opportunities, and posi-tively impacts the lives of the people we engage with, is a prerequisite for long-term success of our business. We focus on DEI because it is the right thing to do – and because it is good for business.” — Mikkel Ipsen VP, Human Resources
 Promethean Energy’s strategy is focused on mature oil and gas assets. Promethean stewards mid- to late-life assets in a continuum from development and production to their end-of-life and decommissioning. Promethean believes high environmental, social and governance standards are critical for the success of Promethean. They reflect the company’s values, address expectations of stakeholders, and support organizational and operational excellence.
Promethean Energy’s strategy is focused on mature oil and gas assets. Promethean stewards mid- to late-life assets in a continuum from development and production to their end-of-life and decommissioning. Promethean believes high environmental, social and governance standards are critical for the success of Promethean. They reflect the company’s values, address expectations of stakeholders, and support organizational and operational excellence.
Early-stage companies are heavily focused on business development and safe execution of activities. Promethean attaches additional importance to building out governance, corporate infrastructure and appropriate policies.
Promethean has implemented a series of policies including a Code of Conduct and Ethics, and a Supplier Code of Business Conduct. As a privately held company, Promethean has established a charter for a Board of Advisors and appointed two advisors to that board.
Finally, Promethean identified the material environmental, social and governance topics currently relevant for its business, and which underpin the Sustainability Framework it has developed.
Sustainability Framework
Promethean incorporates the following policies, goals, and processes into its governance and in contractual arrangements with partners and counterparties.
Priorities
Environment
- GHG Emissions: Promethean measures and reduce emissions.
- Spills and Leaks: Promethean ensures structured health, safety, and environment management systems are in place.
- Waste, Re-use, Recycling: Promethean applies the waste hierarchy to decision-making: reduce, re-use, recycle, recovery, landfill.
- Emissions to Air: Promethean minimizes emissions to air in line with best practice.
- Habitat and Biodiversity Impacts / Site Restoration / Impact on Other Uses: Promethean includes these considerations when assessing options including for rigs to reefs and Net Environmental Balance Analysis (NEBA) impacts.
- Water: Promethean’s goal is to minimize negative impacts on water resources.
Social
-
- Health and Safety: Promethean ensures structured health, safety, and environment management systems are in place.
- People, Diversity, Training and Development, Employee Engagement: Promethean wishes to deliver a working environment across the value chain that encourages collaboration, transparency, and a workforce that draws on the best talent available, regardless of race, nationality, religion, gender, age, sexual orientation, marital status, or disability.
- Human Rights, Human Trafficking and Modern Slavery: Promethean is committed to respecting human rights and to mitigating risks associated with modern slavery and human trafficking.
- Anti-bribery and Corruption: Promethean has adopted an anti- bribery policy.
- Community Impacts: Where Promethean’s work makes use of or shares resources and environments with communities, the goal is to maximize positive net impacts.
Governance
- Contract Governance: Promethean has transparent, collaborative, and aligned governance to facilitate cost-effective, timely and safe execution of activities.
- Risk Management: Promethean applies integrated risk management taking account of risks wherever they exist in the chain.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Promethean ensures operations and performance are informed by relevant stakeholder input.
- Sustainability Framework: Addressing material environmental, social and governance risks and opportunities through the lens of the Framework helps deliver on legal and contractual responsibilities, Promethean’s strategy and values.
- Climate Risk Governance: Promethean takes account of both physical and transition risks and opportunities arising from climate change
 Measuring The Carbon Footprint
Measuring The Carbon Footprint
SEACOR Marine strives to be a part of the solution in the world’s transition to a lower-carbon economy by reducing emissions across its business operations. Aligned with its sustainability and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals, SEACOR Marine continues to invest in reliable, safe, and green transport solutions, along with technology and software to improve operations and minimize environmental impact.
By measuring both direct and indirect emissions and employing digitization and digitalization for data standardization, automation, aggregation, and analysis, SEACOR Marine gains a comprehensive understanding of its environmental impact. This approach enables the identification of areas for further operational improvement. Supporting the maritime industry's shift toward digitization and automation, SEACOR Marine embraces digital technologies and solutions to enhance operational efficiencies and achieve decarbonization goals. The continued installation of Electronic Fuel Measuring Equipment supplied by FUELTRAX across the entire fleet allows real-time fuel monitoring and advanced data analytics, enhancing vessel operational efficiency and significantly reducing carbon emissions.
Through its development with Spinergie of a carbon intensity indicator (CII) metric adapted for offshore supply vessels, SEACOR Marine is able to determine the annual reduction factor needed for continuous improvement in emissions across its fleet. This CII tool aggregates, analyzes, and standardizes inputs to provide an accurate snapshot of a vessel’s fuel consumption and energy efficiency, guiding operations and contributing to future designs. Although the utilization of this CII measurement tool has not been made mandatory for vessels under 5,000 gross tons, SEACOR Marine’s commitment to reducing emissions goes beyond regulations and it will continue to hold itself to a higher standard.
Moreover, SEACOR Marine's continued implementation of Spinergie's digital platform across its fleet, Smart Fleet Management, provides real-time visibility into fleet performance, focusing on intelligent reporting, operational tracking, and actionable key performance indicators. This platform allows SEACOR Marine to evaluate the underlying operational drivers behind direct emissions, including the influence of speed, cargo, crews, weather and operating requirements from charters. Implementing the Smart Fleet Management platform has allowed SEACOR Marine to observe the environmental impact of its fleet and to use the platform's data to arrive at a carbon intensity number as a baseline for further improvements, driving operational efficiencies and reduced costs.

Harnessing Renewable Energy
In recognizing the crucial role of renewable energy in the global energy transition, SEACOR Marine remains dedicated to investing in green technology solutions and exploring various fuel alternatives. SEACOR Marine’s platform supply vessels (PSV) equipped with hybrid battery power systems (Hybrid PSV) provide solutions that reduce fuel consumption and emissions by up to 20%. As of June 2023, SEACOR Marine owned and operated nearly 10% of the global fleet of 70 Hybrid PSVs, with plans to further investment in hybrid battery power systems. SEACOR Marine continues to evaluate projects for its transition to the future, including cold ironing in port using green hydrogen-powered fuel cells or auxiliary generator sets and Power-to-X technology through harnessing green hydrogen and hybrid stored energy solutions.
Commitment to Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
SEACOR Marine’s commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion is evident through its employee-led Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Committee. This committee assists the Sustainability Council in fostering an environment that attracts talent, encourages innovation, ensures a supportive work environment, and values diversity. SEACOR Marine’s Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Statement underscores its dedication to providing a workplace free from discrimination, harassment, and retaliation. Mandatory training for all employees covers discrimination and harassment prevention policies, recognizing stereotypes and biases, and respecting different viewpoints and life experiences. As an equal opportunity employer, SEACOR Marine makes hiring and employment decisions based on merit, qualifications, and abilities, fostering a culture that promotes a sense of belonging among its diverse talent base.
 SLB Workforce Development Program
SLB Workforce Development Program
At SLB, people are the first value and the company is committed to promote development and inclusion for all, as well as to serve in the communities where they live and work. SLB believes in the power of a diverse workforce, which fuels innovation through varied perspectives, skills, and experiences, enhancing problem-solving and yielding better outcomes for our teams and business.
One significant initiative reflecting this commitment is SLB’s tailored workforce development program for underserved communities. The aim is to empower individuals with pertinent skills through personalized training and mentorship, aligning curriculum with our local job demands. This focus on soft and technical skills, coupled with ongoing support, not only secures initial job placements but also aims for long-term career growth.
This commitment is reflected in various initiatives:
- Workforce Development: Tailored for native Alaskans.
- Internship Programs: Catering to high school students with disabilities.
- Employee Resource Group (ERG) Council: Advocating for and supporting employees.
- Partnerships: Collaborations with organizations like Noah’s House in Houston, TX and Fletcher Technical Community College in Schriever, LA.
Collaborating with local communities provides a skilled talent pool, fostering innovation and community ties. Impacting over 40 individuals in 2023, SLB takes pride in meeting workforce needs while empowering communities through sustainable employment opportunities. SLB is committed to driving both personal and communal growth through initiatives and recognize the value a diverse team brings.
 SLB is committed to quantifiably reducing the environmental impact of operations in the oil and gas industry, without compromising performance. The SLB Transition Technologies portfolio comprises technologies and services across SLB that enables customers to significantly improve sustainability and avoid emissions in their operations, while simultaneously driving traditional values of performance, reliability, and quality.
SLB is committed to quantifiably reducing the environmental impact of operations in the oil and gas industry, without compromising performance. The SLB Transition Technologies portfolio comprises technologies and services across SLB that enables customers to significantly improve sustainability and avoid emissions in their operations, while simultaneously driving traditional values of performance, reliability, and quality.

Using a scientific methodology developed by SLB engineers, the impacts of these technologies have proved to reduce footprint. In 2022, SLB was awarded the SEAL Environmental Initiatives Award in recognition of their leadership in reducing greenhouse gas emissions in oil and gas operations through low carbon technologies.
SLB launched many of these new technologies in their North America Offshore operation in 2023 and saw a 20% increase in the implementation of this portfolio year on year. A few examples of these include subsea boosting systems, drilling fluids, waste management, and reservoir testing technologies.

Increasingly adopted across SLB operations, these innovative technologies not only exemplify the company’s commitment to environmental stewardship but also underscore their dedication to delivering sustainable solutions without compromising industry-leading performance systems, drilling fluids, waste management, and reservoir testing technologies.
 Emissions Reductions
Emissions Reductions
TechnipFMC is more than a global leader in the energy industry – TechnipFMC is a leader with a vision. TechnipFMC works to enhance the industry’s performance and drive real change through relentless innovation and global collaboration, and does this in safe and responsible ways. The TechnipFMC team’s work constantly strengthens ESG culture, laying foundations for a better future.
A commitment to emissions reduction
In 2020, TechnipFMC announced the 50 by 30 commitment to reduce Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 50 percent by 2030. It has three focus areas:
- Purchase energy and fuel from renewable sources
- Increase energy efficiency
- Adopt technologies that support the decarbonization journey
TechnipFMC Vessels (OneFleet)
TechnipFMC’s Subsea business deploys a state-of-the-art fleet specialized in a wide range of field activities to support client projects with reliable assets, people, equipment, and expertise.
OneFleet’s GHG emissions account for more than 75 percent of the company’s Scope 1 and 2 emissions. Finding ways to reduce the fleet’s emissions is essential to the success of TechnipFMC’s 50 by 30 commitment. OneFleet’s decarbonization plan is being rolled out to reduce fuel consumption and emissions, thereby minimizing the environmental impact, improving operational efficiency, and reducing cost.
OneFleet’s decarbonization plan highlights the importance of the Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan (SEEMP) introduced in 2013 by the International Maritime Organization (IMO). The company’s crews embraced the challenge of bringing SEEMP ‘to life’ – proactively seeking opportunities to improve efficiency, reduce the amount of machinery online, and operate leaner at higher loads.
Thanks to engagement and collaboration internally and with clients, vessels are transiting at speeds that optimize fuel efficiency - reducing fuel consumption and lowering emissions.
A fleet-wide digital platform provides operational insight and energy consumption awareness. The platform’s dashboard (Figure 1) enhances data accuracy and informs decision-making to achieve significant reductions in fuel consumption and emissions.
The decarbonization plan includes technological upgrades, such as battery hybridization. In 2021, Deep Arctic (Figure 2) – a Dynamic Positioning Class 3 Dive Support Vessel (DSV) – became the industry’s first battery-hybrid DSV. Battey hybridization reduces annual fuel consumption and corresponding emissions by approximately 18 percent.
 OneFleet also assessed the impact of alternative fuels on vessel engines and is ready to use them in compliance with applicable law or where otherwise commercially viable, which would further reduce Scope 1 emissions. OneFleet continues to evaluate opportunities to collaborate with clients to use low-carbon sustainable fuels, such as Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil (HVO) blends. OneFleet keeps abreast of the latest regulatory developments and is involved in industry groups to better understand and assess new requirements.
OneFleet also assessed the impact of alternative fuels on vessel engines and is ready to use them in compliance with applicable law or where otherwise commercially viable, which would further reduce Scope 1 emissions. OneFleet continues to evaluate opportunities to collaborate with clients to use low-carbon sustainable fuels, such as Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil (HVO) blends. OneFleet keeps abreast of the latest regulatory developments and is involved in industry groups to better understand and assess new requirements.
Overall impact
TechnipFMC’s OneFleet has welcomed a step change in carbon-conscious decisions, and we will continue to evaluate further actions that can deliver material and sustainable reductions in both fuel consumption and GHG emissions.
 TGS provides data, intelligence, advanced processing, analytics, cloud-based data applications, and other specialized services and solutions to energy companies across the energy spectrum, whether it is oil and gas, carbon capture and storage, solar or wind development. TGS has the world’s largest integrated subsurface data library that includes seismic data, magnetic and gravity data, multibeam and coring data, digital well logs, and production data from deep-water offshore to conventional and unconventional plays worldwide.
TGS provides data, intelligence, advanced processing, analytics, cloud-based data applications, and other specialized services and solutions to energy companies across the energy spectrum, whether it is oil and gas, carbon capture and storage, solar or wind development. TGS has the world’s largest integrated subsurface data library that includes seismic data, magnetic and gravity data, multibeam and coring data, digital well logs, and production data from deep-water offshore to conventional and unconventional plays worldwide.
TGS has a global presence to support customers in any market with corporate headquarters in Oslo, Norway; and operational headquarters in Houston, Texas, USA; and with additional offices located in Brazil, Australia, United Kingdom and Canada.
TGS Summer Internship Program
Being a leading energy data and intelligence company, TGS recognized the need for diverse skill sets to keep pace with the evolving landscape of the industry. Further, there is a collective need across our industry to attract junior workers who may not fully appreciate the opportunities available to them within our industry. TGS’ comprehensive summer internship program not only provides valuable career development experiences to students, but also serves as a talent pipeline for the future of our industry and company.
TGS interns are recruited from universities across the US, UK, and Norway as well as other countries where we have offices, and given the opportunity to work on real-life, TGS projects that contribute to the company's success in areas of data analytics, offshore wind, imaging, and business development. For example, some of our intern projects provided contributions to TGS’ MDIO technology that is the underpinning of our Data Verse offering, while other interns’ projects provided key input to advance our Wind Axiom platform. At the end of the program, the interns present their work to the company in office-wide presentations, showcasing how their work advances TGS. This approach not only benefits the interns by providing practical experience but also adds value to TGS by tapping into diverse perspectives and skill sets.
A critical aspect of our internship program is recruiting candidates from various academic backgrounds in both undergraduate and graduate programs who are pursuing degrees in a variety of fields beyond geoscience such as data science, technology, and environmental studies. TGS also pairs each intern with a mentor within their department and a TGS “buddy” in a different department, and ensures the interns meet with the different business units across the company to get full exposure to all the opportunities available to them within this industry.
The success of TGS's internship program is evident in the rate at which interns are hired for full-time positions after graduation: 100% of the interns accept jobs offered at TGS following the end of their internship. By providing a platform for students to showcase their abilities and contribute meaningfully to the company during their internships, TGS has created a seamless transition from student life to professional employment.
The key impact and benefits of the TGS Summer Internship Program include:
- Diversity of Thought: The internship program has brought in fresh perspectives and ideas, enhancing the company's ability to innovate and adapt to industry changes.
- Skill Diversification: TGS now boasts a workforce with a broader skill set, allowing the company to tackle challenges and explore opportunities beyond the traditional scope of the oil and gas sector.
- Employee Recruitment and Retention: Interns who have transitioned into full-time roles are likely to have a higher level of job satisfaction and loyalty, having already experienced the company culture and workflow during their internships
TGS’ summer internship program fosters a culture of inclusivity and generates a critical pipeline of innovative talent to continue to position TGS as an industry leader in embracing the changing face of the energy industry.
Using Vessel Emissions Data to Achieve Efficiency Gains
In 2019, TGS committed to supporting the Climate Action Sustainable Development Goal (SDG 13) and began to track and report on vessel emissions as part of our strategy to ascertain our carbon footprint and reduce emissions. TGS utilizes Maress, a cloud-based digital management system owned by VPS-Decarbonisation, on every vessel it charters to provide real-time information on the vessel’s emissions and fuel consumption. Prior to the use of Maress, emissions data was manually derived using self-reported fuel consumption data, allowing for increased human error and operational inefficiencies.
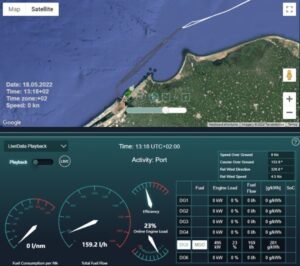 Since Maress’ implementation two-and-a-half years ago, TGS has collected sufficient emission and fuel consumption data from multiple vessels to establish fuel consumption and emission baselines, thus allowing TGS to benchmark performance on a vessel-by-vessel basis, visualize related outputs through the Maress dashboards, and make operational decisions that take into account fuel consumption and emissions impact. This has resulted in new efficiency gains being recognized and implemented.
Since Maress’ implementation two-and-a-half years ago, TGS has collected sufficient emission and fuel consumption data from multiple vessels to establish fuel consumption and emission baselines, thus allowing TGS to benchmark performance on a vessel-by-vessel basis, visualize related outputs through the Maress dashboards, and make operational decisions that take into account fuel consumption and emissions impact. This has resulted in new efficiency gains being recognized and implemented.
For example, by analyzing and comparing fuel consumption and emission trends for TGS’ chartered vessels against similar types of vessels, TGS recognized that better fuel consumption efficiency and emission reductions are achieved by chartering vessels built within the past 15 years. When chartering vessels, TGS aims to prioritize newer vessels where possible, subject to other factors including vessel availability, to achieve fuel consumption efficiencies and reducing the carbon footprint.
TGS continues to work closely with VPS-Decarbonisation on how to utilize the Maress system to make sustainable operational decisions that take into account fuel consumptions and emissions.
NOIA ESG Network 2024 Report


