
National Ocean Industries Association (NOIA) report, The Offshore Energy Industry’s Innovation & Workforce Excellence Report, showcases the remarkable advancements and commitments of the offshore energy sector in innovation, environmental stewardship, and workforce development, featuring 16 case studies.
NOIA President Erik Milito said, “This report not only reflects our industry's dynamic progress but also our commitment to smart, efficient, and responsible energy production. American offshore energy production is where innovation meets environmental responsibility, and this report, with its 16 comprehensive case studies, is a testament to that achievement. We’re not just meeting expectations—we’re surpassing them, pushing technology forward and empowering our world-class workforce. That drive runs through every level of our industry, from the Gulf of America to the Atlantic coast and beyond, reflecting a shared commitment to excellence.”
The Offshore Energy Industry’s Innovation & Workforce Excellence Report At a Glance
The report features case studies from NOIA member companies:
- American Bureau of Shipping (ABS)
- Danos
- Equinor
- Exmar Offshore
- Fugro
- Kosmos
- Noble
- Ørsted
- SEACOR Marine
- Seadrill
- SLB
- Talos
- TechnipFMC
- TGS
- Valaris
- The NEED Project
Innovation at the Forefront: With sections like "The Future of Offshore Innovation," the report delves into cutting-edge projects such as the 20k Projects in the Gulf of Mexico, highlighting how the industry is pushing boundaries in ultra-deep water exploration.
Commitment to Sustainability: The document underscores the sector's dedication to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles, offering insights into carbon capture, use, and storage (CCUS), and sustainable offshore transport and operations.
Workforce Excellence: Emphasizing durability and safety, the report features initiatives from industry leaders, showcasing how companies are nurturing the next generation of energy professionals.
Fostering Education Initiatives: NOIA’s dedication to ESG extends to educational initiatives through our long-standing partnership with the National Energy Education Development (NEED) Project. For over 25 years, this collaboration has aimed at enhancing energy education, including in the realm of offshore energy.
Policy and Regulatory Insights: It provides an analysis of the current regulatory landscape affecting ESG reporting and investment, crucial for stakeholders navigating this space.
Awards and Recognition: The report celebrates the achievements of companies like TechnipFMC, SEACOR Marine, and LLOG and SLB, who have been recognized for their exemplary practices in ESG and safety.
 The National Ocean Industries Association launched its new Environmental, Social, & Governance (ESG) program, The NOIA ESG Network, in January 2020 as a platform for learning, collaboration, and continued improvement in ESG. ESG and ESG investing present both expectations and opportunities for the offshore energy community. ESG has taken its lumps over the past year, as investors realign their priorities and reassess financial metrics. However, the fundamental importance of environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and corporate governance, respectively, continues to be a priority for the broad stakeholder community. According to Oxford professor Robert Eccles:
The National Ocean Industries Association launched its new Environmental, Social, & Governance (ESG) program, The NOIA ESG Network, in January 2020 as a platform for learning, collaboration, and continued improvement in ESG. ESG and ESG investing present both expectations and opportunities for the offshore energy community. ESG has taken its lumps over the past year, as investors realign their priorities and reassess financial metrics. However, the fundamental importance of environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and corporate governance, respectively, continues to be a priority for the broad stakeholder community. According to Oxford professor Robert Eccles:
It’s been a rough few years for ESG—the popular shorthand for measuring and managing a company’s environmental, social, and governance performance. In the United States the term has become a punching bag for both sides of the political aisle. For those on the left, ESG doesn’t go far enough in forcing business to address major societal challenges, particularly climate change. For those on the right, it represents an insidious attempt to make companies adopt a liberal agenda, thus distorting markets and free competition…. Yet the need for a transparent way to connect a company’s financial performance with its environmental, social, and governance performance remains.
Whether it is investors, customers, or employees, high results in environmental, social, and governance performance can serve to elevate your industry above other sectors and your company above your competitors. And, despite its recent stumbles, ESG continues to provide a tremendous opportunity for offshore energy companies to amplify their success and overall performance in the ESG factors to all stakeholders, ranging from investors to the public at large. NOIA’s ESG network serves that precise purpose by bringing the industry together to share, learn, collaborate, and highlight our industry’s collective excellence and high performance in environmental, social, and governance areas. Each sector of the offshore energy industry embodies our collective commitment to outstanding performance.
Offshore Oil & Gas
The groundbreaking work in the Gulf of America, like Chevron’s Anchor project, which kicked off oil production in August 2024, underscores this industry's relentless pursuit of excellence. Anchor is the first deepwater high-pressure development to achieve production, employing groundbreaking 20,000 psi subsea technology to access reservoirs at depths of 34,000 feet.
Such achievements are built on collaboration across the industry. Chevron’s Anchor development, for example, relied on Transocean’s state-of-the-art Deepwater Titan, an eighth-generation drillship equipped with a 1,700-ton hoisting system, a 20,000-psi well control system, and a 10,000-psi mud system—the first of its kind in the world.
Other high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) projects, including Beacon Offshore Energy’s Shenandoah and bp’s Kaskida, are poised to follow suit, unlocking critical resources that bolster U.S. energy security and economic vitality.
The American offshore industry is full of innovators contributing to the solutions and best practices that optimally balance societal and environmental needs. Their success is reflected in hard data, which continues to convincingly show that the U.S. offshore industry, in the Gulf of America, brings to market critical barrels of oil that are among the lowest carbon intensity in the world.
In 2023, NOIA released a groundbreaking report by ICF entitled the “GHG Emission Intensity of Crude Oil and Condensate Production.” The report finds that U.S. oil production, particularly in the U.S. Gulf of America, has much lower carbon emissions intensity than much of the rest of the world.
According to ICF, increasing total U.S. production to a level that offsets foreign crude and condensate would result in a 23% reduction in the average international carbon intensity. In the Gulf of America, the American advantage is much more striking. Increasing Gulf of America U.S. production to offset foreign crude or condensate would lead a whopping 46% decrease in emissions intensity per barrel.
In terms of carbon emissions intensity, U.S. oil production outperforms foreign producers like Russia and Iran by a wide margin. The Gulf of America is a powerful source of energy that rises above foreign sources as an ideal energy choice, particularly given the current, turbulent geopolitics of energy.
The findings from ICF can be added to the growing body of work from other leading organizations that have found that the U.S. Gulf of America is at the forefront of delivering among the world’s lowest carbon intensity barrels of oil.
The U.S. Gulf of America produces lower carbon intensity barrels because it is a thriving energy production system. Offshore operations in the U.S. Gulf of America are carried out in adherence to among the most comprehensive safety and environmental standards. Through a cutting-edge technological revolution, the U.S. Gulf of America continues to innovate new solutions to enhance operational efficiency and reduce emissions.
A massive amount of energy is produced with a remarkably small and efficient footprint. For example, there are 18 deepwater facilities in the Gulf that combine to equal roughly the size of 9 city blocks and that produce roughly the same amount of oil as the entire state of North Dakota.
The data also demonstrates that offshore production has a lower per-unit rate of methane emission as compared to offshore. While methane has a much shorter atmospheric life than carbon dioxide, methane is understood to have a larger warming potential. Managing methane emissions is key in mitigating climate change.
Thanks to the level of scale and sophistication of technology, offshore wells have a much higher average well productivity and this leads to lower methane emissions per unit of production. Methane emissions are tightly controlled for U.S. offshore operations. Companies are required to recover and sell all produced gas, and venting and flaring is directly regulated by the U.S. Department of the Interior. Gas detection systems are deployed widely on facilities to quickly detect and address leaks, and companies are deploying advanced technologies that include Forward Looking InfraRed (FLIR) cameras, drones, and advanced software systems to further prevent methane emissions.
Offshore Wind
There has also been progress in developing new offshore wind projects in the U.S. The South Fork Wind project, a joint venture between Ørsted and Eversource, is New York’s first offshore wind farm and the first commercial-scale offshore wind farm in federal waters. With 12 turbines generating 132 MW of renewable energy, South Fork Wind will power approximately 70,000 homes.
Other offshore wind projects are not far behind, which is great news for local onshore residents and workers throughout the nation. While the power generated from offshore wind projects may be local, the economic significance, including the supply chain, has a national footprint. States like Louisiana, Texas, North Carolina, and Florida have already realized jobs and investments from supporting offshore wind projects.
Consider the ECO Edison, the first-ever American-built, owned, and crewed offshore wind service operations vessel (SOV), constructed by Edison Chouest. This vessel will play a pivotal role in the operation and maintenance of wind farms, serving as a base for technicians and equipment.
Built by over 600 workers across shipyards in Louisiana, Mississippi, and Florida, and sourcing components from 34 states, the ECO Edison exemplifies the significant financial investments and collaborative efforts driving the U.S. offshore wind industry forward. Furthermore, there is an additional pipeline of more than $14 billion in proposed additional investments to ports, manufacturing, vessels, workforce development, and research.
According to a November 2024 report by the LSU Center for Energy Studies, capital expenditures are estimated to range between $63 billion and $142 billion through 2050. The study also provides that, over the next decade, offshore wind construction is estimated to support an annual average of over 43,000 to over 80,000 total jobs per year in the respective scenarios. The study projects a range of installed offshore wind capacity between 23 gigawatts (GWs) and 52 GWs. Once fully operational, an estimated 33,000 to 73,000 jobs will be supported nationwide annually. This is estimated to support $1.9 billion to $4.3 billion in earnings per year, and $3.3 billion to $7.4 billion of GDP per year respectively, of offshore wind capacity will be constructed in the U.S.
Offshore Carbon Sequestration
Carbon capture and storage is recognized as a key tool in the toolkit for emissions reduction efforts. The International Energy Agency calls CCS “an important opportunity to achieve deep carbon dioxide emissions reductions.” The U.S. Gulf of America could very well soon be the leader in CCS. Early projections show that 50 million tons of C02 annually could be stored beneath the Gulf of Mexico by 2030, more than all the CCS currently operating globally. The Gulf’s storage capacity could double by 2040.
The technical and commercial feasibility of large offshore storage projects is being proven on the global stage. The first large-scale CO2 capture and injection project with dedicated CO2 monitoring and storage was commissioned at the Sleipner offshore gas facility in Norway in 1996.
Today, the facility has stored more than 20 MtCO2 close to at 1 km depth under the North Sea. With operations beginning in 2024, Northern Lights is a new CCS project under construction that will initially store up to 1.5 million tons of CO2 per year with the goal to achieve 5 million tons of CO2 per year by 2027. The Northern Lights project is part of a larger carbon capture and storage initiative that will capture CO2 from industrial sources within Norway, ship liquid CO2 from capture sites to an onshore terminal on the coast, and then transport the CO2 by pipeline to an offshore storage site below the North Sea in water depths of more than 300 meters and total depth to injection of 2,500 to 3,000 meters. In the U.S., the Gulf of America is well suited for the development of projects like Northern Lights.
The U.S. Gulf of America offshore region provides tremendous advantages for an emerging U.S. CCUS sector. The Gulf of America is characterized by vast geologic prospects for CO2 storage, extensive and established energy infrastructure along the Gulf Coast and throughout the outer continental shelf, a proximity to industrial centers for capturing emissions, and an assessable engineering and energy knowledge base and workforce, along with associated RD&D capabilities.
Collaboration Across All Sectors
The collaborative nature of our industry’s work is now in full effect through NOIA, with dozens of companies, representing oil and natural gas operators, wind producers, drilling contractors, geophysical services, marine construction, manufacturers and suppliers, the service sector, and offshore service vessels placing their names on the NOIA ESG Network Participation Agreement. Importantly, all members of NOIA benefit from our ESG program, which serves as the foundation for advancing the diverse objectives of the association, from advocacy to energy dialogue to collaboration. Content and conversation that focuses on environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and corporate governance is now embedded activities of NOIA.
This report reinforces the strength in the performance of the offshore energy industry across the ESG spectrum, highlighting our industry as a key investment pillar of our economy in providing the energy that truly lifts society.

ABS ESG Initiatives: Advancing Sustainability in Offshore Energy
Introduction
As a leading classification organization, ABS is deeply committed to supporting sustainability and innovation in the offshore energy sector. ABS’ Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) initiatives align with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and address the industry’s pressing need for decarbonization, safety and environmental stewardship. Through advanced research, global collaboration and cutting-edge technologies, ABS is driving the transformation of offshore energy systems towards a safer and more sustainable future.
Environmental Leadership
Sustainability Centers and Research
ABS has established a network of sustainability centers across the globe, each dedicated to developing innovative solutions for the offshore and marine sectors. These include:
- Houston: Focused on alternative fuels, energy analytics and hydrogen technologies. Recent achievements include expanding hydrogen feasibility studies and supporting regulatory agencies with decarbonization strategies.
- Copenhagen: Specializing in vessel innovations and fuel technologies, contributing to projects like onboard carbon capture and safety studies for ammonia and nuclear fuels.
- Singapore: Pioneering ESG reporting frameworks and green shipping corridor initiatives, such as partnerships between Singapore and Los Angeles/Long Beach.
Decarbonization Technologies
ABS is at the forefront of the offshore industry’s decarbonization efforts. ABS provides technical expertise and supports the adoption of decarbonization technologies including:
- Alternative Fuels: ABS is leading the adoption of alternative fuels such as hydrogen, ammonia and methanol. Projects include approval in principle (AIP) for offshore hydrogen and ammonia production platforms and storage systems for compressed hydrogen.
- Electrification: The ABS Electrification Center supports projects like hybrid-electric vessels and cold-ironing solutions for ports. Collaboration with industry leaders, including Sea Forrest Power Solutions, has advanced fire-resilient battery designs and other safety measures.
- Carbon Capture: ABS has issued approvals for innovative onboard carbon capture systems and liquefied carbon dioxide (LCO2) carriers, ensuring safe and efficient transportation of captured emissions.
- Offshore Wind and Nuclear Energy: ABS provides technical guidance and AIPs for floating offshore wind turbines and nuclear-powered offshore platforms. These innovations expand renewable energy production and offer scalable solutions for decarbonization
Social Responsibility
Workforce Development
At ABS, people are at the core of their mission. ABS fosters an inclusive and collaborative workplace and invests in talent development through training, internships and mentorship programs.
Scholarship Program
ABS demonstrates its commitment to education and workforce development through its global scholarship program. In 2023, ABS donated over $1.4 million in the form of scholarships to over 45 universities globally. Award recipients are current undergraduate and graduate students with majors in fields ranging from ocean engineering and naval architecture to computer science and cybersecurity. This program not only supports academic growth but fosters the next generation of professionals who will lead innovation and sustainability efforts in the offshore energy sector.
Community Engagement
ABS supports the communities it serves through global scholarship programs, local volunteerism, and initiatives like the United Way Campaign. These efforts underscore our commitment to enriching society while advancing the offshore energy industry.
Safety Excellence
Safety remains a cornerstone of ABS operations. In 2023, ABS achieved a 10% reduction in total recordable injuries and enhanced safety training programs across all regions. ABS’ proactive approach ensures that decarbonization advancements maintain the highest safety standards for offshore workers.
Governance and Innovation
ESG Blueprint
To guide the offshore industry’s sustainability journey, ABS has developed an ESG Blueprint. This framework offers best practices for incorporating ESG principles into operations, with a focus on regulatory compliance, emissions reduction and data transparency.
Partnerships and Collaboration
ABS actively collaborates with stakeholders across the maritime value chain, including partnerships with the Mærsk Mc-Kinney Møller Center for Zero Carbon Shipping, the Global Maritime Forum and the Blue Sky Maritime Coalition. These alliances enable the development of viable pathways to net-zero emissions.
Digital Innovations
- ABS Wavesight™:
- Leveraging software platforms like My Digital Fleet and eLogs to enhance fleet efficiency and compliance.
- Supporting emissions reporting under frameworks like the Poseidon Principles and Sea Cargo Charter.
- Green Shipping Corridors:
- ABS utilizes advanced simulation technologies to model green shipping corridors, optimizing fuel use, bunkering resources, and emissions management.
Offshore-Specific Highlights
Blue Economy Leadership
ABS is a key advocate for sustainable practices in offshore energy. This includes decommissioning oil and gas platforms responsibly, enabling offshore wind development, and guiding the establishment of offshore spaceports for future innovations.
Supporting the Energy Transition
- Hydrogen Hubs: ABS is facilitating the integration of hydrogen hubs into offshore infrastructure, enabling cleaner energy production and storage.
- Decommissioning Expertise: Through partnerships with CENPES and others, ABS supports environmentally responsible decommissioning of offshore assets, minimizing ecological impacts.
Conclusion
ABS is proud to lead the offshore energy industry toward a sustainable future. By combining technical expertise, innovative technologies and a commitment to social and environmental responsibility, ABS is empowering stakeholders to navigate the energy transition with confidence. ABS’s ESG initiatives exemplify its mission to protect life, property and the natural environment—ensuring a resilient and prosperous offshore energy sector for generations to come.
 Danos Coastal Restoration: Driving Innovation in Artificial Reef Creation
Danos Coastal Restoration: Driving Innovation in Artificial Reef Creation
Danos is proud to be at the forefront of coastal restoration and efforts to enhance marine habitats through the production, installation and deployment of advanced artificial reef systems. With a commitment to environmental stewardship and collaboration, Danos has partnered with leading organizations to support projects that restore vital fisheries and habitats, protect coastal communities, and promote biodiversity in marine environments across the Gulf South.
Innovative Solutions for Coastal Restoration
Danos fabricates and installs cutting-edge artificial reef products, including proprietary Natrx ExoForm™ modules, known as “Cajun Coral.” These lightweight, modular structures are designed for efficiency, environmental compatibility, and scalability, offering numerous advantages:
- Cost-Effective & Environmentally Friendly: Cajun Coral requires less material, has a smaller installation footprint, and causes minimal disturbance to natural habitats during production and deployment.
- Advanced Technology: Using 3D printing technology, Danos produces Cajun Coral modules at scale for diverse applications, including shallow and deepwater environments. This technology can be adapted and deployed globally, thanks to Danos’ location with direct access to the Intracoastal Waterway and Gulf of Mexico.
- Support for Biodiversity: Artificial reefs support marine habitat restoration efforts, including oyster seeding and long-term support for fish populations and other aquatic life.
In addition to Cajun Coral, Danos has worked with Reefmaker to install Super Reefs at deeper locations in the Gulf of Mexico. Super Reefs are made from limestone rocks that are the perfect pH for all marine life to live.
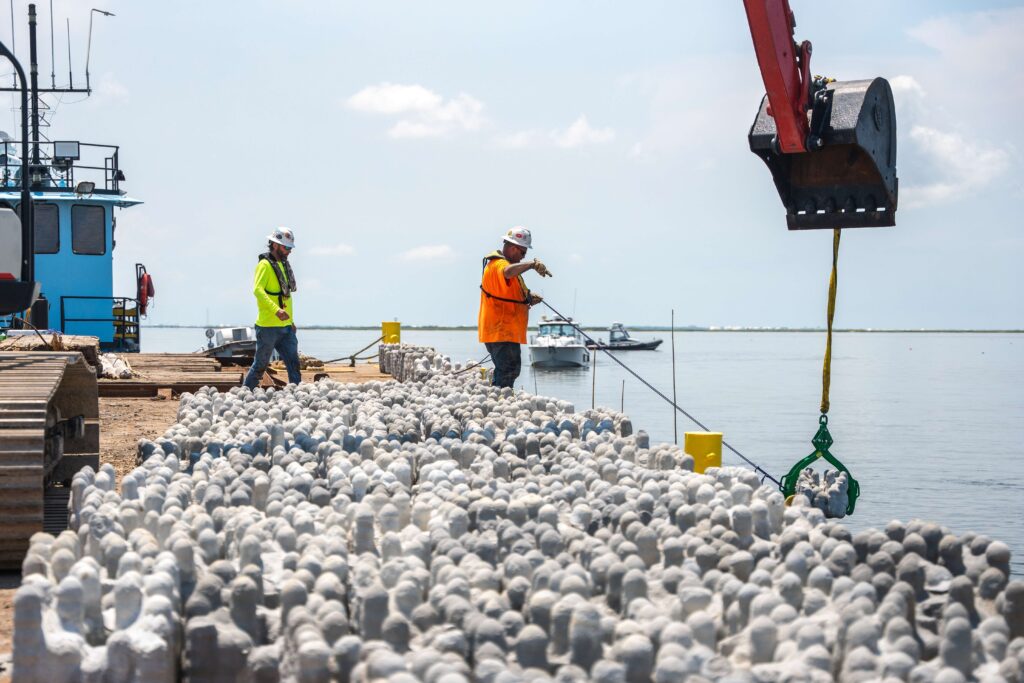 To date, Danos has installed over 50,000 square feet of reef products, leveraging innovative solutions to replace vital habitats lost to natural and manmade causes. These efforts protect barrier islands and marshes, which serve as natural defenses against storm surges and flooding, reducing vulnerability for coastal communities and infrastructure.
To date, Danos has installed over 50,000 square feet of reef products, leveraging innovative solutions to replace vital habitats lost to natural and manmade causes. These efforts protect barrier islands and marshes, which serve as natural defenses against storm surges and flooding, reducing vulnerability for coastal communities and infrastructure.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
Danos’ coastal restoration projects deliver tangible benefits for local communities and ecosystems:
- Restoring Marine Habitats: Vital marine habitats are being renewed, benefiting a wide range of species and rejuvenating ecosystems.
- Boosting Local Economies: These efforts support the local fishing community, enhance recreational fishing, and boost fishing-related tourism revenue, while also generating employment opportunities in areas such as fabrication, installation, and project management.
- Promoting Sustainable Growth: Artificial reefs provide a foundation for long-term ecological health, supporting sustainable fisheries and biodiversity.
Danos Owner and CEO of Danos Ventures Eric Danos stated, “Together with our partners, we are committed to ensuring that future generations of sportsmen and women can enjoy the great fishing experiences that our waterways offer. This project not only restores vital habitats but also strengthens the connection between our community and the natural environment that we care about.”
Project Highlights: 2024 Success Stories
Danos’ Coastal Restoration service line achieved significant milestones in 2024, participating in five major artificial reef projects that illustrate its commitment to collaboration and sustainability.
Pelican Island Reef – January 2024
In Timbalier Bay, LA, Danos partnered with Chevron, Natrx, and the Coastal Conservation Association (CCA) of Louisiana to install a new artificial reef aimed at reviving fish populations and supporting recreational anglers. The project utilized Cajun Coral modules fabricated by Danos, demonstrating the scalability and effectiveness of these structures in marine habitat restoration.
Ted Beaullieu Sr. Reef Expansion – June 2024
As part of the CCA Louisiana’s 50th artificial reef milestone, Danos contributed 43 concrete cylinders and recycled materials to the Ted Beaullieu Sr. Reef in South Marsh Island Block 233. Additionally, Danos deployed 100 Cajun Coral modules to create a four-acre habitat supporting species like trout and redfish. This project underscores Danos’ role in addressing habitat loss from decommissioned oil and gas platforms.
Raising Cane’s Hotel Sid Reef – August 2024
Danos fabricated and installed over 500 Cajun Coral modules to create 10,000 square feet of living reef near Grand Isle, LA. Funded by Raising Cane’s founder Todd Graves, this project restored a historic fishing site while supporting redfish, speckled trout, and flounder populations. The reef demonstrates the ecological and economic benefits of collaborative restoration initiatives.
South Timbalier Block 63 Reef – November 2024
Danos partnered with CCA Louisiana, the Louisiana Department of Wildlife and Fisheries (LDWF), Chevron, and Reefmaker to install 36 Super Reefs in South Timbalier Block 63. These structures, made of concrete, steel rebar, and limestone, include both 8-foot and 15-foot pyramids designed to study size preferences among marine species like snapper. Monitoring efforts aim to optimize future reef designs for maximum ecological benefit.
South Timbalier Block 86 Reef – December 2024
For CCA Louisiana’s South Timbalier 86 Reef, Danos installed 36 Super Reefs. The reef included 12, 15-foot pyramids weighing over 30,000 pounds each, and 24, 8-foot pyramids weighing 6,000 pounds each. These structures provide critical habitat for snapper and other marine life, enhancing biodiversity and supporting sustainable fishing opportunities.
 Commitment to Collaboration
Commitment to Collaboration
Danos’ coastal restoration success is driven by strong partnerships with conservation organizations, private companies, and government agencies. Collaborative efforts like these enable the development of innovative, nature-based solutions to combat habitat loss and ensure the sustainability of Gulf Coast fisheries. Funding from LDWF’s Artificial Reef Trust Fund and support from CCA’s REEF Louisiana Program have been instrumental in these achievements, along with partnerships with companies like Natrx and Reefmaker.
Looking Ahead
As Danos continues to advance its coastal restoration initiatives, the company remains committed to developing best practices to address the challenges facing marine ecosystems. With several projects already planned for 2025, Danos is poised to build on its legacy of innovation, environmental stewardship, and community impact.
 Using Cutting-Edge Technology to Responsibly Monitor the Marine Ecosystem
Using Cutting-Edge Technology to Responsibly Monitor the Marine Ecosystem
The development of offshore wind projects is not only about delivering much-needed renewable energy to the grid and strengthening U.S. energy security—it also exemplifies cutting-edge innovation, engineering, and technology. Yet few are aware of the extent to which offshore wind developers have applied those very same qualities to mitigating the industry’s impact on the surrounding marine environment.
The dynamics of marine populations in the wild have long been challenging to characterize. Successful detection and protection of marine mammals such as whales and dolphins, species by their nature that only spend short periods of time at the surface of the water, requires a multi-pronged approach. Fundamental biological questions about their populations, such as how many individuals are present in a given area and their activities (e.g., feeding, migrating, or mating)—can be even more challenging.
In the past, efforts to detect and quantify marine mammals have relied almost exclusively on human observation aided by visual tools such as binoculars and cameras. While these classic techniques do offer valuable information during the period in which observers are deployed onboard vessels or airplanes, they are inherently limited to short observation periods typically measured in hours or, at best, days at a time and often constrained by weather, seas and other factors. The bottom line is that continuous monitoring of these species is simply impossible using traditional human observers alone. A range of newer and more sophisticated technologies can be deployed to help fulfill our responsibility to work sustainably within the marine ecosystem.
Equinor early on recognized the need for additional technology to properly characterize marine mammal populations in the Empire Wind lease area located in federal waters of the New York Bight. After Equinor acquired the lease in 2017, there was a clear need to establish a robust baseline of marine animals present in the lease area in order to properly plan our project and mitigate potential sound impacts from the eventual installation of foundations for our turbines. This recognition led Equinor to partner with experts and, beginning in 2019, fund activities by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute (WHOI). The funding both supported and built upon joint WCS/WHOI deployments of underwater listening devices known as Passive Acoustic Monitoring (PAM) buoys.
PAM buoys are sophisticated devices equipped with hydrophones (underwater microphones) capable of detecting and recording marine mammal vocalizations. Built to endure harsh ocean conditions for up to a year with minimal maintenance, these buoys provide near real-time data on vocalizations to scientists and decision-makers. These vocalizations indicate which species are present and provide information about their behavior. When combined with visual observations and population modeling techniques, the acoustic data provides invaluable insights into the activities of these marine animals.
The data from this effort doesn’t just go to a select group of experts; readings from the WCS/WHOI PAM buoys are also available online for public consumption. By sharing this near real-time data with the public, Equinor, the WCS and WHOI provide broader access to information that informs broader marine mammal mitigation measures in the New York Bight. For example, the data supports voluntary slow zones that are broadcast out to mariners, reducing the risk of lethal collisions when certain animals are detected.
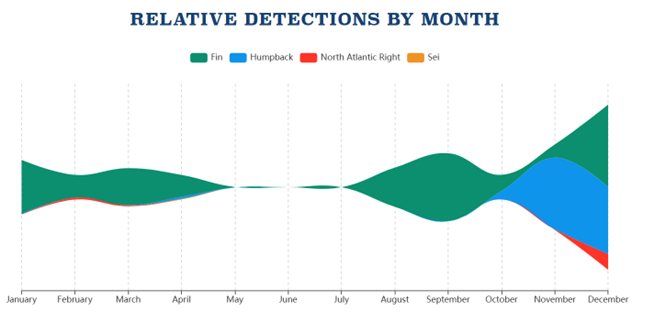
Source: https://whalesofnewyork.wcs.org/Explore-the-Data/Analysis
The partnership with WCS and WHOI is an integral component of Empire Wind’s marine mammal monitoring and mitigation program and is set to play an invaluable role as Equinor prepares to install foundations to support the wind turbines in 2025. The initiative has been a high priority for Equinor, which has enlisted expert scientists from WCS and WHOI—along with others from Duke University, the University of New Hampshire, the University of Rhode Island and the New England Aquarium—to help evaluate our proposed measures for protecting and monitoring marine mammal populations. Beyond our continued support for the WCS/WHOI PAM buoys, these measures include investments in the use of infrared cameras, human observers, real-time sound field verification, sound-dampening technologies, and ongoing partnerships and information exchange with scientists from Duke University’s highly respected Project WOW (wildlife and offshore wind) initiative.
Empire Wind’s comprehensive mitigation program will be underway upon the start of foundation installation in May 2025. Ongoing updates and findings will be shared to advance understanding of these important species. Equinor is excited to engage in this initiative for sophisticated data-gathering, information sharing, and responsible development as Equinor works to provide New York with a reliable and robust new source of energy to help meet growing energy demand.
 The Exmar OPTI® Series: Flexible, Scalable, Repeatable
The Exmar OPTI® Series: Flexible, Scalable, Repeatable
Exmar Offshore Company (“EOC”) is committed to minimizing its environmental impact through the development and implementation of cutting-edge technologies in the offshore industry. One such technology that continues to drive growth for EOC and for the offshore floating industry as well as adhere to the interest in Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) is the proprietary and patented Exmar OPTI® semisubmersible design. This design has allowed EOC to deliver under license, a standardized hull solution to its clients that aids in the efficient, fast, and safe execution of projects while maintaining a constant push towards structural optimization. This structural optimization that’s ingrained in the OPTI® design reduces carbon dioxide emissions by reducing steel usage and maintaining total topsides payload considered in several areas of a semisubmersible life cycle from steel production, construction, transportation, and installation. With 3 OPTI® designed semisubmersibles currently installed in the Gulf of Mexico, 1 currently under construction, and 1 in the detailed design engineering phase, the OPTI® is a complete project solution that is proven, flexible, scalable, and repeatable with uncompromising safety, quality, and cost. To provide an example of just how much the OPTI® design can save in carbon dioxide emissions, the optimized design of the 3 OPTI® semisubmersible platforms currently installed reduced their emissions by 45,792 tons of carbon dioxide compared with the industry average for similar facilities. This amount is equivalent to the carbon dioxide emissions of 10,000 passenger cars in a year or the emissions of transporting 6,400 tons of air cargo by plane from Europe to the United States. With 1 facility scheduled for installation in 2025 and another in execution, these figures will continue to increase.
Scalable and Flexible by Design
EOC has invested in extensive research and development resulting in proprietary and patented structural designs for areas on the OPTI® hull such as the pontoons and columns. These designs have allowed for a complete offshore solution which in turn has demonstrated the OPTI® to be a proven success for clients. The OPTI® is a scalable and flexible design meaning the design can accommodate a wide range of payload capacities as well as allow for easy deck truss and hull alignment and mating. Because of this scalability and flexibility, the OPTI® can be deployed in any water depth and the design readily lends itself to global fabricator capabilities. The OPTI® further benefits the industry as it is provided under license agreements, which means that lessons learned from each project are captured for the benefit of future developments and the result is that ESG-related gains are leveraged to any Operator utilizing this design.
Ease of Construction and Repeatable Design
The OPTI® has been designed to facilitate ease of construction where the hull columns, pontoons, and nodes are repeatable and scalable for both the designer and the fabricator. Minimal structural shapes, thicknesses, and steel material grades are selected to reduce steel weight and improve fabricator efficiency thus resulting in an optimization of the structure’s steel usage while not compromising structural integrity or payload capacity. Leveraging these advantageous features, from initial engineering contract, an OPTI® facility can be moored on site in less than 3 years.
Superior Hydrodynamic Performance
The innovative design of the OPTI® has established superior hydrodynamic performance for the semisubmersible. At its core is a proprietary ring pontoon shape, engineered to optimize stability and efficiency in challenging marine environments. Complementing this is the unique multi-sided column configuration that leads to significant reductions in drag forces resulting in lower mooring forces and negligible vortex induced motions. Additionally, this proprietary column shape provides collision safe, accessible, and hydrodynamically shielded mounting surfaces for piping, pump caissons, and umbilicals.
Innovative FAST® Riser Installation System
A key component of the OPTI® semisubmersible design is its FAST® (Fully Aligned by Stress joint Trimming) installation system. The FAST® system exploits the geometry of the deck and pontoon, along with ballast movement, to align the riser and proprietary porch adapter. The full FAST® riser installation process is accomplished offshore without hot work or cofferdams and with minimal diver intervention that supports a faster and safer operation. To date EOC has used the FAST® Riser Installation System over 20 times, which has saved clients time and resources in an important step for offshore production efforts.
Commitment to Sustainability and Client Success
EOC’s commitment to innovation and offshore floating solutions spans the entire asset lifecycle, from concept to operational support, ensuring client needs are met while prioritizing ESG initiatives.

 Remote and autonomous operations: enhancing safety, sustainability, and workforce opportunities
Remote and autonomous operations: enhancing safety, sustainability, and workforce opportunities
Fugro maps, models, and monitors the natural and built environment, delivering the critical Geo‑data and analysis needed to build and operate offshore energy projects. To meet the sector’s growing demand for Geo-data while prioritizing safety and sustainability, Fugro increasingly delivers its services remotely, leveraging advances in robotics, automation, and cloud computing. This approach contributes to Fugro’s goal of achieving net-zero carbon emissions for its marine operations (scopes 1 and 2) by 2035.
How remote operations work
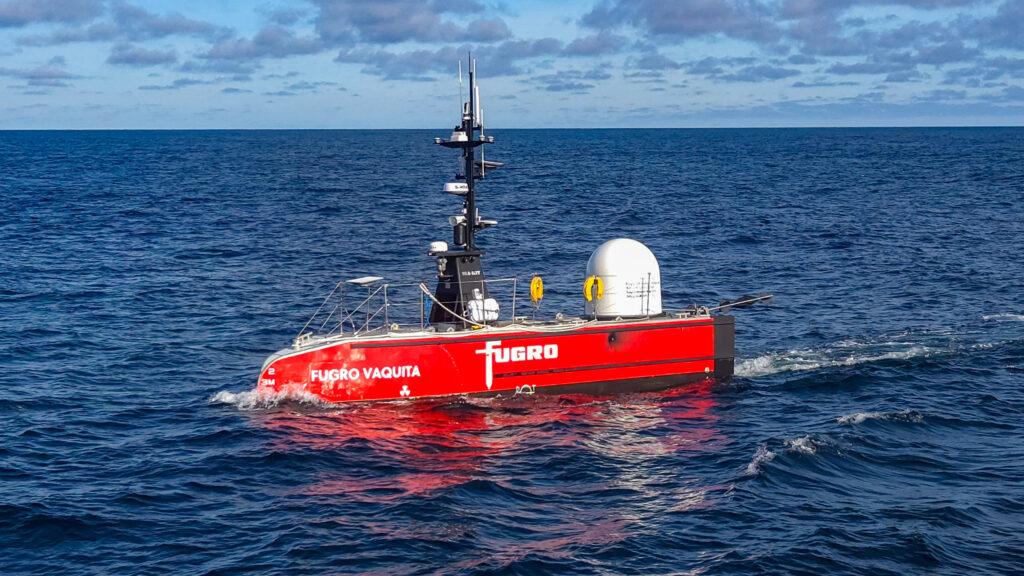
Fugro maintains a global network of high-tech remote operating centers (ROCs) where expert staff remotely command and control vessel-based equipment to conduct survey applications from the safety and comfort of an onshore office environment. These services support optimizing and de‑risking offshore infrastructure design; precisely positioning the installation of subsea and floating infrastructure; and performing inspections of offshore assets from construction to decommissioning.

Where regulations permit, the ROCs also enable fully autonomous surveys and inspections using Fugro’s state-of-the-art Blue Essence® uncrewed surface vessels (USVs), equipped with its Blue Volta® electric remotely operated vehicles (eROVs). Previously offered in Australia, Europe, and the Middle East, the solution will make its Americas debut in Brazil during Q1 2025. Fugro is also collaborating with U.S. government agencies to advance USV operations domestically. For example, in 2024, the company contributed to a U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) report entitled “Coast Guard: Autonomous Ships and Efforts to Regulate Them.”
What are the benefits?
Fugro’s transition to remote operations offers numerous benefits for both the company and its clients. Near real-time Geo-data access, enabled by cloud computing, streamlines internal workflows while also accelerating external project timelines through faster decision-making. Additionally, remote operations improve worker safety by minimizing personnel exposure to offshore hazards.
The reduction in personnel travel and the use of smaller vessels also contribute to a significant decrease in the environmental impact of operations. Lightly crewed vessels can lower CO2 emissions by more than 50% compared to vessels with large accommodation capacities. USV deployment further enhances safety and sustainability, eliminating the need for offshore survey personnel entirely and reducing CO2 emissions by as much as 95% compared to traditional vessels.

Building the future workforce
Remote operations are not only transforming how Fugro delivers Geo-data, this new way of working is also addressing a critical challenge facing the offshore industry: attracting and retaining a skilled workforce. Traditionally, offshore operations have involved extended periods away from home, making it difficult for many individuals to pursue a career in this field. By enabling people to work from shore-based offices, remote operations expand the talent pool, attracting individuals from diverse backgrounds. This also improves work-life balance, making careers in ocean science and technology more appealing to a broader range of individuals, including younger generations.
Ready for growth in the US
In October 2024, Fugro celebrated a significant milestone: 10 years and one million hours of successful remote operations globally. Notably, half of these hours were logged by Fugro’s U.S. operations, which pioneered the company’s remote operations journey in the Gulf of Mexico. This initiative, launched during a period of declining energy prices, provided clients with safe and cost-effective positioning services for rigs and other work vessels.
A decade later, Fugro has further solidified its commitment to remote operations in the US by relocating its Houston-based ROC from the city's southwest quadrant to the Energy Corridor. This strategic move enhances collaboration within the energy sector by placing the ROC at the heart of industry expertise. Housed in a data center built to Miami-Dade resilience standards, the new ROC boasts robust communication and power backups, ensuring business continuity even during severe weather events. This state-of-the-art facility provides a robust platform for continued growth and innovation in remote operations, including the use of USVs when federal guidelines allow.
 Driving industry transformation
Driving industry transformation
Remote and autonomous technologies are revolutionizing work offshore, and Fugro is leading this charge. By embracing digital innovation, Fugro is not only improving the efficiency and safety of offshore projects but also creating a more sustainable and inclusive future for the industry. Through advancements in remote operations and the increasing adoption of USVs, Fugro is paving the way for a new era of marine exploration and development, one that is characterized by enhanced safety, reduced environmental impact, and greater access to a diversified workforce.
 SHARING EXPERIENCES TO MAKE THE OFFSHORE INDUSTRY SAFER
SHARING EXPERIENCES TO MAKE THE OFFSHORE INDUSTRY SAFER
In June 2024, a high-pressure nitrogen cylinder ruptured spontaneously on the deck of a vessel working for Kosmos Energy in the Gulf of Mexico. The blast was potentially fatal but, thankfully, only first aid injuries were sustained.
Kosmos Energy's Gulf of Mexico team responded with urgency to make the workplace safe by removing all other cylinders. With a deep sense of unease about the incident lingering within the company's HSE and Gulf of Mexico teams, Kosmos Energy approached the incident investigation and follow-up from the viewpoint of anticipating where else it could happen, potentially with much more serious consequences.
The cylinder that ruptured was held in a rack along with 11 others. This one cylinder ruptured with such force that it demolished the rack in which it was housed, moved the remnants of that rack across the deck, and in the process displaced the other cylinders housed in the rack up to 50 feet away.
Cylinder rupture was initiated by external corrosion at the base. Several other cylinders were observed to have suffered similar external corrosion. Kosmos Energy believes that this is a wider problem that requires urgent action, including revision of industry practice for external visual inspection of cylinders in relation to inspecting rack assemblies.
The key findings of the incident investigation:
- The cylinders had been visually inspected by the supplier in accordance with industry guidance prior to being loaded onto the rig. However, the severe corrosion that caused the rupture was not spotted during this inspection.
- The cylinder that ruptured was located in the middle of the quad and therefore not easy to inspect without disassembly. As Kosmos Energy looked deeper into the matter, the company learned that racks of connected cylinders are often not disassembled during inspections.
 This potential barrier to inspection is now under discussion with the Department of Transportation and the Compressed Gas Association.
This potential barrier to inspection is now under discussion with the Department of Transportation and the Compressed Gas Association.
Representatives from Kosmos Energy are talking to each of these bodies to share what they have learned and to advocate for change. Kosmos Energy is also sharing what it has learned from this experience across the industry with the goal of raising awareness about how serious a problem this could be.
The company estimates that across 250 oil and gas offshore rigs there are probably up to 25,000 cylinders in use at any one time. This means there are a lot of cylinders in circulation with inspection practices that may not be fit-for-purpose, especially when accounting for the harsh offshore marine environment with its moisture and salt.
Kosmos Energy is extremely fortunate that only minor injuries were incurred. But the company sees this incident as a warning that reinforces the need to maintain a sense of unease, and as a catalyst for revising industry practice.
Kosmos Energy has shared its learnings with its Gulf of Mexico and international JV partners around the world, and with 40+ other operators and suppliers. The company has also talked to:
- U.S. Department of Transportation
- U.S. Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement
- Offshore Operators Committee
- International Association of Oil and Gas Producers
- Energy Institute
- International Association of Drilling Contractors
- Compressed Gas Association
The takeaways Kosmos Energy has emphasized:
 Kosmos Energy is modeling safety leadership behavior and encouraging everyone in the industry to get answers to these questions.
Kosmos Energy is modeling safety leadership behavior and encouraging everyone in the industry to get answers to these questions.
The answers may help save a life.
 Harnessing Energy Efficiency Insights to Drive Sustainable Offshore Operations
Harnessing Energy Efficiency Insights to Drive Sustainable Offshore Operations
In a time where our industry must sing to a new tune of responsible drilling operations, it is critical to engage every ‘hand on deck’ in the journey of sustainability. Driving meaningful change in the topic of sustainability involves transitioning from implementing ideas and standards from a watchtower to approaching change from the bottom-up. Sustainable change requires not only a change of activity but a change in mindset which is cultivated through empathy and understanding of each rig hand’s ability to contribute to more efficient operations.
The main purpose of the EnergyWise program is to reduce energy consumption through sustainable operations, thereby enabling the achievement of our greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction target by 2030. To achieve an expected 6% reduction in energy consumption through the adoption of sustainability behaviors, thoughtful engagement supported by knowledge sharing and recognition has allowed Noble (thus far) to identify over 100 offshore behaviors that can reduce our fuel consumption.
Stepping into the molds that Safety programs have casted from the last decade, the EnergyWise program utilizes tools and processes used for safety observations to incorporate a feedback mechanism for energy management. Every member on a rig, employee or third-party, has the ability to identify an energy consumption risk or opportunity and submit for further investigation by a rig-based team and onshore team.
With the establishment of Rig Sustainability Committees, a rig-based team is trained on tracking and monitoring fuel consumption to recognize trends and opportunities for efficiency. This allows the teams to quantify potential impacts and test hypotheses for fuel consumption savings.
The program has also paved a path of engagement with the rig to grow an energy management system compliant with ISO standards.
Within 6 months, over 400 EnergyWise alerts have been received across our fleet from recognizing positive behaviors, identifying opportunities for energy efficiency, innovative ideas for upgrades and even additional areas on the topic of sustainability in which Noble can exemplify being a responsible driller such as waste management and reducing single-use plastics.
Critical to the program is establishing a two-way engagement to drive the adoption of the sustainability mind-set and champion energy efficient energy management from all levels of the organization. This is the key to achievable change while fostering ownership from every role on the rig.
 Offshore Wind Is Driving Investment in Construction, Shipbuilding, Manufacturing
Offshore Wind Is Driving Investment in Construction, Shipbuilding, Manufacturing
Across the country, Ørsted’s $20 billion planned investments in American energy are creating thousands of jobs, revitalizing ports, supporting energy independence, and providing opportunities for suppliers and employers across the energy sector to help build the future of American energy infrastructure.
Ørsted’s 924-megawatt Sunrise Wind off the coast of New York is already making history as the state’s largest offshore wind project, delivering economic benefits statewide and bringing local companies into the industry. On Long Island, local contractor Haugland Energy Group is building Sunrise Wind’s onshore transmission system as part of a $200 million supply chain award that is creating more than 400 local union jobs. This work is further supported by local employers LS Cable and Elecnor Hawkeye, which installed and jointed the onshore cables.
In Upstate New York, Ørsted is investing $86 million to construct advanced foundation components for Sunrise Wind, further expanding the domestic energy supply chain. This work is creating more than 230 jobs in areas such as construction and steel manufacturing, from the Capital Region to Western New York, with suppliers including Riggs Distler and Ljungstrom.
Ørsted is establishing a permanent operations and maintenance hub in East Setauket, NY, and a harbor facility in Port Jefferson, NY, strengthening Long Island’s position as a national offshore hub. With the aim of supporting current and future projects, Ørsted is investing $10 million in the new National Offshore Wind Training Center in Brentwood, Long Island, where workers will gain skills to build careers in offshore wind.
In New England, the company has made significant progress this year constructing Revolution Wind, the nation’s first multi-state offshore wind project, which will power hundreds of thousands of homes in Rhode Island and Connecticut. As with Sunrise Wind, this progress is made possible thanks to hundreds of local workers and hundreds of millions of dollars in local investments.
Rhode Island’s ProvPort was once a leading industrial center in the Northeast, and today it is an important economic hub again thanks in part to Ørsted’s ongoing investments in the Ocean State. More than 125 local union workers built foundation components for Revolution Wind in ProvPort, following similar work for Ørsted’s operational South Fork Wind project. Dozens of jobs were created constructing the facility itself, with work overseen by longtime Rhode Island building leader Dimeo Construction.
Importantly, these projects are fueling new opportunities for America’s shipbuilding industry. Offshore wind service vessels built in shipyards from New Orleans to Philadelphia are sustaining local crews of technicians, many of whom will service Ørsted’s projects for decades to come. As one example, the first U.S.-built offshore wind service operations vessel, the ECO EDISON, was launched in 2024, built by more than 600 workers in Louisiana, Mississippi and Florida, with components sourced from 34 states. The ECO EDISON is busy today supporting Ørsted’s Northeast projects.
In Connecticut, Ørsted and its partners have invested more than $100 million to revitalize New London’s State Pier, where the company is marshaling turbines for its Northeast projects. As a result of investments into the facility, vessel activity is increasing at State Pier and generating high-skilled, long-term employment in New London.
Ørsted’s Northeast portfolio is proof that investing in American offshore wind is about more than generating electricity and securing energy independence. It’s about creating jobs and supporting local economic activity. Revolution Wind and Sunrise Wind alone are creating more than 2,000 direct jobs -- in addition to thousands more indirect and induced jobs -- and providing opportunities for longstanding American energy, manufacturing, and construction leaders to participate in this new American energy industry.
Ørsted is investing in America’s energy workforce. The company has developed and deployed an offshore wind workforce credentialing program to support local worker transitions in Rhode Island and New York. To date, more than 335 union workers have received a range of certifications including Helicopter Underwater Escape Training and Global Wind Organization Basic Safety Training. The growing pool of certified workers will benefit the U.S. offshore wind industry as it scales up and hires more skilled workers.
As Ørsted looks to the future and continues deploying $20 billion of planned investments into America’s energy industry and supply chain, it is committed to building on progress to date in the offshore wind market and continuing to advance projects that are transformative for our nation’s energy security, independence and economic growth. Offshore wind is a proven job-creator supporting a national supply chain spanning 40 states, and Ørsted is proud to be America’s offshore wind leader.

 Leveraging Digitization and Digitalization
Leveraging Digitization and Digitalization
Supporting the maritime industry's shift toward digitization and automation, SEACOR Marine embraces digital technologies and solutions for data standardization, automation, aggregation and analysis, to gain a comprehensive understanding of its environmental impact, enhance operational efficiencies and support the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) decarbonization goals.
SEACOR Marine continues to install Electronic Fuel Measuring Equipment supplied by FUELTRAX and Smart Fleet Management supplied by Spinergie across its fleet. By using real-time fuel monitoring and advanced data analytics, together with leveraging client data from disparate systems and third-party data sources, SEACOR Marine gains comprehensive real-time visibility into fleet performance, focusing on intelligent reporting, operational tracking and actionable key performance indicators. This allows us to enhance vessel operational efficiency, significantly reduce its carbon emissions and support behavioral change within the fleet regarding fuel usage.
Notably, through its work with Spinergie, SEACOR Marine has contributed to the creation of a carbon intensity indicator (CII) calculation for offshore support vessels. The CII tool will allow the industry, and SEACOR Marine, to aggregate, analyze and standardize manual, mechanical and automatic inputs to give an accurate snapshot of a vessel’s fuel consumption and energy efficiency to guide operations and create an information feed into vessel upgrades and future designs. The IMO has officially supported and approved the utilization of the CII as a viable approach for quantifying and reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions stemming from maritime vessels. Although the utilization of this measurement tool has not been made mandatory, SEACOR Marine’s commitment to reducing emissions goes beyond regulations and SEACOR Marine will continue to hold itself to a higher standard.
SEACOR Marine’s ability to accurately measure and report its emissions is a crucial step towards achieving its sustainability goals and demonstrating its commitment to transparency and accountability. By standardizing, automating, aggregating and analysis of data through digitization and digitalization, SEACOR Marine will gain a comprehensive understanding of its environmental impact and identify areas where it can improve its operations further.
Hybrid Battery Power Systems
 SEACOR Marine recognizes the crucial role that renewable energy plays in the global energy transition, and that this process begins with meaningful innovations. This unwavering commitment has positioned SEACOR Marine as one of the market leaders in platform supply vessels (PSVs) equipped with hybrid battery power energy storage systems (Hybrid PSVs) and SEACOR Marine takes pride in being the sole owners of Hybrid PSVs operating in the offshore sector beyond the North Sea and Gulf of Mexico. SEACOR Marine currently owns and operate approximately 8% of the global fleet of 88 Hybrid PSVs (per Clarksons Research Services World Offshore Register as at December 12, 2024), SEACOR Marine has four additional Energy Storage Systems (ESS) on order that are expected to be installed on four PSVs, and have committed to the building of two new Hybrid PSVs with scheduled delivery fourth quarter of 2026 and first quarter of 2027.
SEACOR Marine recognizes the crucial role that renewable energy plays in the global energy transition, and that this process begins with meaningful innovations. This unwavering commitment has positioned SEACOR Marine as one of the market leaders in platform supply vessels (PSVs) equipped with hybrid battery power energy storage systems (Hybrid PSVs) and SEACOR Marine takes pride in being the sole owners of Hybrid PSVs operating in the offshore sector beyond the North Sea and Gulf of Mexico. SEACOR Marine currently owns and operate approximately 8% of the global fleet of 88 Hybrid PSVs (per Clarksons Research Services World Offshore Register as at December 12, 2024), SEACOR Marine has four additional Energy Storage Systems (ESS) on order that are expected to be installed on four PSVs, and have committed to the building of two new Hybrid PSVs with scheduled delivery fourth quarter of 2026 and first quarter of 2027.
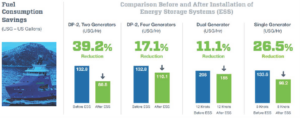
Hybrid PSV Case Study: Fuel Consumption Savings
 Supporting Renewable Energy Clients
Supporting Renewable Energy Clients
SEACOR Marine continues to service renewable energy clients through its investment in liftboats, walk-to-work gangways and continual improvement in operational efficiencies, and SEACOR Marine stands to benefit from the growth of offshore wind energy markets, particularly in the United States. SEACOR Marine’s liftboats offer a more efficient solution for wind turbine generator feedering, wind farm installation, hydraulic directional drilling operations, maintenance and repair, and accommodation facilities, compared to deploying multi-purpose service vessels. Where conditions and water depth permit, its liftboats can operate in an elevated position, allowing us to shut down all main engines and rely on a single generator during the project. This approach significantly reduces fuel consumption compared to vessels that need to run all engines to maintain position. By utilizing liftboats, SEACOR Marine is able to provide support for offshore wind projects while reducing the environmental impact of clients and operations.
 As a company committed to sustainability, SEACOR Marine understands the importance of supporting the energy transition while addressing the environmental impact of the offshore oil and gas industry. As such, SEACOR Marine is committed to contributing to the safe decommissioning of offshore wells and platforms for the reduction of methane emissions and preservation of the marine environment. SEACOR Marine’s liftboats are ideally positioned and fully equipped to support decommissioning efforts in the Gulf of Mexico. Liftboats provide a cost-effective and efficient solution for plug and abandonment operations, platform decommissioning and hydraulic directional drilling operations, by elevating out of the water and reducing fuel consumption.
As a company committed to sustainability, SEACOR Marine understands the importance of supporting the energy transition while addressing the environmental impact of the offshore oil and gas industry. As such, SEACOR Marine is committed to contributing to the safe decommissioning of offshore wells and platforms for the reduction of methane emissions and preservation of the marine environment. SEACOR Marine’s liftboats are ideally positioned and fully equipped to support decommissioning efforts in the Gulf of Mexico. Liftboats provide a cost-effective and efficient solution for plug and abandonment operations, platform decommissioning and hydraulic directional drilling operations, by elevating out of the water and reducing fuel consumption.
Reducing Waste
SEACOR Marine's proactive approach to waste reduction encompasses a comprehensive strategy aimed at minimizing its ecological footprint across various dimensions and setting a benchmark for environmental stewardship.
SEACOR Marine’s campaign of reducing plastic waste includes the Safe Water On Board (SWOB) initiative, involving the installation of water purification units on vessels and providing crew with insulated stainless-steel reusable water flasks. SEACOR Marine is proud to highlight that the SWOB initiative has saved an estimated 132,215 single-use plastic bottles from landfill, equating to approximately 3,150 kilograms (or 6,944 pounds) of plastic (as at March 19, 2024).
Other waste reduction initiatives include water conservation, paper waste, culinary waste and cleaning product waste. SEACOR Marine continue to install digital solutions on its vessels employing 100% biodegradable and environmentally friendly cleaning products, reducing cleaning product waste. SEACOR Marine’s culinary-focused training programs aim to curtail food waste, complemented by investments in technologies such as ethylene filters to extend the shelf life of perishable items.
 Seadrill utilizes advanced technologies that enhance drilling efficiency while reducing environmental impact. Through targeted application of Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD) and Advanced Generator Protection (AGP) systems, Seadrill’s operations achieve measurable improvements in both technical capability and emissions reduction. These implementations build on years of offshore operational experience and technical innovation.
Seadrill utilizes advanced technologies that enhance drilling efficiency while reducing environmental impact. Through targeted application of Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD) and Advanced Generator Protection (AGP) systems, Seadrill’s operations achieve measurable improvements in both technical capability and emissions reduction. These implementations build on years of offshore operational experience and technical innovation.
Managed Pressure Drilling
Seadrill is an expert in Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD), an advanced drilling technique that enhances environmental protection while improving operational efficiency. The system's precise control of annular pressure profiles throughout the wellbore significantly reduces environmental risk through enhanced pressure control and early kick detection, helping prevent well control incidents that could impact marine environments.
The system's ability to drill within narrow pressure windows reduces the volume of drilling fluids needed and minimizes waste generation. Additionally, the enhanced drilling efficiency reduces the overall time required to complete wells, directly lowering emissions from drilling operations.
Historically used in only the highest-complexity wells, Seadrill is now utilizing this technology widely. We have completed over 100 MPD wells globally, achieving increased efficiency, enhanced safety and improved reservoir management for Seadrill’s clients in a wide range of conditions.
By the end of first quarter 2025, we will have equipped nine rigs with MPD capabilities and one with Continuous Mud Level (CML) drilling capabilities, greatly expanding these environmental safeguards and technical capabilities.

Advanced Generator Protection
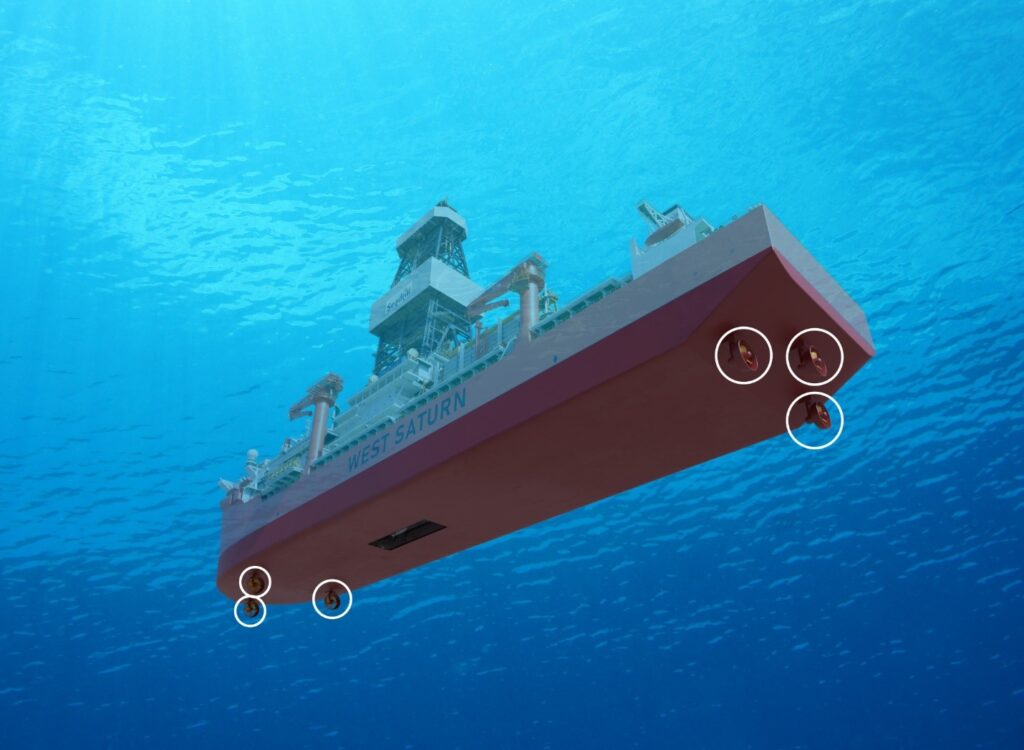
In 2022, Seadrill’s seventh-generation ultra-deepwater drillship, the West Saturn, marked a significant advancement in environmental stewardship with the implementation of Advanced Generator Protection (AGP) technology. This system enables operation of high voltage electrical switchboards in Closed Bus Tie (CBT) configuration, allowing the rig to run more efficiently with fewer engines.
CBT configuration reduces fuel consumption, greenhouse gas emissions and well costs, providing significant benefit to clients:
- Fuel consumption reduced by up to 8%
- CO2 reduction of up to 8%
- NOX reduction up to 10%
- Engine running hours reduced by up to 20%
Following its success on the West Saturn, Seadrill is expanding AGP technology across Seadrill’s global fleet. This systematic approach to emissions reduction demonstrates Seadrill’s commitment to advancing industry sustainability goals through practical, measurable solutions.
Looking Forward
Seadrill is committed to a brighter future for our industry and the planet. MPD and AGP technologies represent a step forward in responsible offshore operations, demonstrating how advanced engineering can protect both operational integrity and environmental interests. Looking forward, Seadrill is focused on expanding these capabilities across Seadrill’s fleet while continuously innovating to reduce carbon intensity, increase efficiency and improve safety performance.
 SLB: Committed to Sustainable Operations
SLB: Committed to Sustainable Operations
As SLB pursues sustainable operations, it is dedicated to achieving NetZero by 2050 through various initiatives and innovations. SLB’s sustainability goals encompass cleaner processes, advanced technologies, and a balanced approach to environmental stewardship. SLB is making investments by deploying water circularity projects, focusing on renewable energy, and bringing cutting-edge transition technologies to their customers.
Circularity
Water circularity is crucial for conserving resources and reducing environmental impact. This year, SLB has achieved a greater than 40% reduction in freshwater consumption year-to-date in North America Offshore operations. SLB’s Clear Flow project in Houma, Louisiana, launched this year, aims to recycle up to 75% of its water, significantly reducing water consumption and carbon footprint.
Renewable Energy
SLB has reduced electricity consumption by more than 10% year-over-year through LED upgrades and energy initiatives. SLB’s transition to renewable energy has led to cutting its facilities' emissions by more than half. Currently, over 40% of SLB’s Gulf Coast facilities operate on renewable energy.
Transition Technology
SLB is committed to reducing the environmental impact of oil and gas operations while maintaining performance. SLB’s Transition Technologies portfolio helps customers enhance efficiency while reducing emissions. In 2024, SLB increased the implementation of these technologies in its North America Offshore operations.
One standout technology is Epilogue, a dual-string barrier evaluation tool that assesses A- and B-annuli without removing the inner pipe during well decommissioning. This method reduces the carbon footprint, operational time, and costs while ensuring regulatory compliance. Approved by BSEE and successfully used in the Gulf of Mexico, it optimizes plugging and abandoning operations, contributing to industry-wide emissions reduction goals. This technology has been recognized with awards from World Oil, ICoTA, OWI, and OTC Spotlight.
https://www.slb.com/driving-energy-innovation
Through these initiatives, SLB continues its commitment to sustainability, ensuring a cleaner and more efficient future for its operations and the environment.
 Building a Safer Tomorrow: Achieving Excellence Through the Talos Competency Assurance and Training Program
Building a Safer Tomorrow: Achieving Excellence Through the Talos Competency Assurance and Training Program
In 2021, Talos launched its Competency Assurance and Training Program under its Safety and Environmental Management System (SEMS). This initiative aims to elevate workforce skills and knowledge through comprehensive training practices, actively engaging employees in mental testing, and assessing their retention and understanding of course materials. This program has played a pivotal role in reinforcing Talos’s company's safety culture.
Knowledge Assessment
Talos begins with a baseline knowledge assessment of its employees and contractors to evaluate their training and ability to retain critical information. These assessments, rated on a scale from 0 to 4, gauge the understanding of specific competency areas. Any score below a particular threshold prompts focused training in that area. Talos’s dedicated team is managing and tracking the competency of over 100 skills for more than 800 individuals.
Benchmarking & Training
The results help to inform the development of targeted plans to address knowledge gaps. One example of a specific gap that was identified in 2023 was in glycol dehydration. The team dedicated 528 hours of in-person training and 1,060 hours of computer-based training (CBT) to bridge this gap, boosting the workforce's confidence and competence in handling glycol dehydration systems.
The initiative led to a 5% improvement in relevant assessment scores, surpassing the industry average. Based on a post-training survey, it also significantly increased employee confidence in handling glycol. In 2024, Talos identified and launched another specialized training course on Oil and Gas Measurement.

Talos’s blended training approach—combining one-on-one competency assessments, computer- based trainings, and interactive in-person classes—caters to different learning styles and allows for the timely delivery of information. Talos’s comprehensive database of CBT modules is online allowing for ease of accessibility. Combining around-the-clock access and multiple methods of learning ensures employees stay updated on the latest safety protocols and industry standards. Leveraging AI software, Talos can also create custom CBT modules to address emerging trends and issues in real-time. In 2023 alone, Talos delivered over 19,000 training hours, marking a 46% increase over 2022.
Results
Talos’s systematic approach to competency assurance, gap analysis, and training by Talos has significantly contributed to safe and efficient operations. Talos has observed an overall decline in its Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR) since the program's inception. In 2023, Talos accomplished a TRIR of 0.45, which was 51% lower than the industry average while completing the acquisition of EnVen Energy Corporation. In the same year, Talos also recorded its lowest Serious Injuries and Fatalities Rate (SIFR) of 0.04. In addition, Talos’s Bureau of Safety and Environment Enforcement (BSEE) inspection performance is also improving year-over-year, finishing 50% below the industry average in 2023. Furthermore, during Talos’s recent BSEE required SEMS audit, this program was identified as a “good practice”.
Ensuring that Talos’s workers are professionally trained and retain that knowledge is a cornerstone of its capacity to deliver exceptional personal and process safety performance. Talos is proud of its progress to improve safety, increase training, and enhance the worker experience. Responsible stewardship guides Talos’s choices every day.


 Leading with Integrity
Leading with Integrity
TechnipFMC’s Sustainability Ambitions
At TechnipFMC, the Sustainability ambition is simple: to drive real, sustainable change that favorably impacts the company, the industry, and the communities where we operate.
TechnipFMC realizes these ambitions through specific measures that help deliver accountability. In 2020, TechnipFMC announced its 50 by 30 target—to reduce its global Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 50 percent by 2030, and established a three-year Scorecard, measured over 2021–2023, with clear, verifiable metrics to drive long-term behavior.
TechnipFMC’s first three-year Sustainability Scorecard concluded on December 31, 2023, and it confirmed the company met or exceeded 10 of the 12 individual objectives.
Continuing the Scorecard approach
TechnipFMC is maintaining the same Scorecard approach for the period 2024 – 2026, believing this approach has resulted in meaningful and sustainable change. After careful consideration based on evidence and evolving priorities, TechnipFMC has adopted new, measurable ESG goals that account for the progress they achieved in their 2021–2023 Scorecard as well as various stakeholder interests. In summary:
- TechnipFMC will introduce three new fully qualified products across its New Energy technology portfolio by the end of 2026. Complementing its commitment to reduce Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions by 50 percent by 2030, they will increase their use of renewable energy.
- Under equal opportunity, it will appeal to an inclusive talent pool by attracting qualified candidates from traditionally underrepresented backgrounds. Through the iVolunteer program, the three-year goal is to achieve 120,0000 volunteering hours in community initiatives. TechnipFMC aims to participate in STEM engagement activities annually in at least 80 percent of the countries in which it operates.
- TechnipFMC will uphold a strong safety culture by rolling out its Safe Choice training and coaching programs. TechnipFMC will ensure at least 50 percent of suppliers identified for human rights assessment each year undergo an on-site audit. Additionally, the company aims to ensure that 100 percent of managers complete annual advanced integrity curriculum training.
While TechnipFMC’s Sustainability scorecard measures specific achievements, the company’s activities extend beyond what is measured on the Scorecard, or to actions and monitoring required by law.
The TechnipFMC Human Rights program: raising the standard for human rights across our industry.
 This collaborative, multi-function program assesses human rights compliance across TechnipFMC’s operations and value chain, consistent with three of the company’s foundational beliefs: sustainability, respect, and integrity. It aims to ensure that everyone in the TechnipFMC ecosystem is treated with dignity, honesty, respect, and fairness.
This collaborative, multi-function program assesses human rights compliance across TechnipFMC’s operations and value chain, consistent with three of the company’s foundational beliefs: sustainability, respect, and integrity. It aims to ensure that everyone in the TechnipFMC ecosystem is treated with dignity, honesty, respect, and fairness.
Through collaboration and increasing transparency, delivering human rights education, and taking remedial action, TechnipFMC enhances worker welfare. The program has helped improve workers’ health and safety, freedom of movement, and individual rights.
Approach
TechnipFMC’s Executive Leadership Team sets the overall Sustainability approach. The Sustainability Steering Committee is responsible for the specific company initiatives toward corporate responsibility, sustainability, climate-related risks and opportunities and actions aimed to further such initiatives.
TechnipFMC also has a Human Rights Working Group and a Human Rights Leaders’ Network.
The working group brings together stakeholders from HSE, People & Culture, Legal & Compliance, and Sourcing & Procurement. This group assessed TechnipFMC’s overall human rights risk at the program’s inception and has since monitored that risk, assessed human rights processes, and managed the human rights metric in the Scorecard.
The leaders’ network brings together support functions, commercial teams, and projects and operations teams to collaborate on human rights initiatives, make process improvements, and develop company-wide standards.
TechnipFMC collaborates with industry counterparts through Building Responsibly to benchmark and raise global standards.
Promoting transparency and accountability, TechnipFMC developed a program database with key performance indicators, and the company records Scorecard goals monthly.
Since inception, the program has regularly assessed members of the TechnipFMC supply chain, which has illuminated and resolved issues such as:
- Retention of identity documents. Reinforcement of migrant workers’ rights to retain, or have unqualified access to, their passport and identity documentation and their right to freedom of movement, including immediate return of workers’ passports and identity documents.
- Withholding of wages. After TechnipFMC’s intervention, backpay was issued to agency workers where the payment of wages failed to meet local legal requirements.
- Grievance mechanisms and access to remedy. Implementation of mechanisms that enable workers to report ethics concerns anonymously, ensure fair and prompt investigation, and prohibit retaliation.
TechnipFMC continuously raises human rights awareness in its supply chain. In 2023, TechnipFMC launched a human rights campaign among suppliers in Malaysia and Singapore. This was extended to Brazil in 2024. So far, TechnipFMC has engaged approximately 60 suppliers in discussions and general awareness.
In April 2023, TechnipFMC partnered with Truckers Against Trafficking to host Combating Human Trafficking – How the Energy Industry Can Make a Difference. This summit brought together representatives from energy and trucking/logistics companies, and law enforcement.
TechnipFMC’s measures ensure it complies with new laws requiring the company to identify and address adverse impacts relating to worker welfare and human rights and publish how it has mitigated potential impacts. Similarly, they help TechnipFMC build trust, meet client expectations, and anticipate evolving legal requirements.
In summary
The TechnipFMC human rights program is built on foundational principles that ensure its effectiveness and impact:
- Simple, precise goal setting. A scorecard sets clear, verifiable metrics that drive performance and promote accountability.
- Risk-based program. Companies should consider their specific circumstances and make appropriate risk-based decisions.
- International standards. TechnipFMC leverages international human rights standards, including the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights.
- Education and collaboration. Collaboration with clients, peers, suppliers, and communities helps TechnipFMC co-develop tools, resources, and practices, and share knowledge and experiences.
- Remediation as a standard. The musician John Lennon said, “There are no problems; only solutions.” Following that ethos, TechnipFMC works with suppliers to raise standards in human rights and act whenever possible.
 “This is TGS”
“This is TGS”
For over 40 years, TGS has built a strong foundation as a global leader in delivering advanced data and intelligence to companies across the energy data value chain, primarily in the oil and gas industry and energy transition industries such as CCUS, offshore wind, solar and geothermal. TGS' integrated offering, driven by leading-edge technology, a broad range of products and an extensive energy data library, makes the company a trusted partner to its clients in the exploration and production of energy resources worldwide.
Noted for its technological innovation, TGS is one of the largest marine seismic survey companies measured by marine 3D acquisition capacity and number of active streamers. TGS manages a fleet of seven active high-end Ramform-designed 3D seismic vessels capable of towing 12 or more streamers and are a leading ocean bottom node (OBN) provider, owning approximately 30,000 high-end OBNs. TGS offers high-end site characterization services for offshore wind energy projects and carbon storage sites through its fleet of 3D streamer vessels and specialized Ultra-High Resolution streamer sets as well as “above-surface” data, such as wind measurements and metocean data, through its multi-client data floating Light Detection and Ranging buoys acquisition campaigns.
TGS’ multi-client library is the largest and most modern in the industry, comprising of over 3.1 million square kilometers of 3D seismic data, 6.28 million line kilometers of 2D seismic data, and 9.5 million digital well logs. TGS’ extensive data library includes seismic data, magnetic and gravity data, multi-beam and coring, digital well logs and production data, wind energy data, data to identify CCUS opportunities and other data related to the renewables sector. Its seismic data library has modern 3D coverage in all significant offshore hydrocarbon provinces of the world.
TGS has approximately 1,700 onshore and offshore employees, with headquarters in Oslo, Norway, and Houston, Texas. Other main offices are located in the UK, Egypt, Brazil, Malaysia, and Australia, with additional employees located in other cities around the globe.
Tackling Environmental Sustainability
“Energy starts with us,” and TGS believes it is their responsibility to help their customers, shareholders and communities in which they live and work shape the future of energy by sustainably conducting operations. TGS is committed to protecting the environment by understanding the energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in its operations and finding ways to reduce its impact, as well as minimizing and mitigating the impact that activities have on the marine and land environments, and communities around them. TGS’s strategy includes:
- Seeking innovative ways to lower emissions from marine and onshore operations, and on-premise data centre operations, to be more energy efficient and use less fuel (e.g. equipment and vessel optimization).
- Utilizing the multi-client business model, which reduces the potential need for duplicative seismic acquisition by licensing the same dataset to multiple customers.
- Diversifying offerings to support the development and production of wind, solar, and carbon capture storage (CCS).
- Repurposing the lithium batteries used in Ocean Bottom Node (OBN) surveys for other purposes rather than disposal reduces waste, and has a positive impact on resource use.
- Protecting marine biodiversity by recovering debris and fishing gear polluting the oceans through the Sustainable Seas Initiative.
What specific initiatives for increasing fuel efficiency were implemented with respect to TGS’ fleet in 2024?
TGS conducted in-depth reviews of vessel equipment and technology, resulting in the testing and deployment of several energy efficiency improvements.

In 2024, TGS implemented engine performance optimization by balancing engine load against the number of engines onboard, resulting in enhanced power output while reducing fuel consumption. Also, TGS saved energy consumption by using a variable frequency drive, which optimized the stopping and starting fans, pumps, and other equipment in the engine room. TGS deployed propeller boss cap fins on Ramform Hyperion and Tethys, and by using the smaller fin attachment and reducing the propeller hub vortex, this resulted in a 40% fuel reduction at 12 knots and up to 5% in fuel savings. Lastly, TGS also changed vessel lighting to LED bulbs to promote energy conservation and made upgrades to rope fairing and hull cleaning to combat build-up, which reduced in-sea equipment drag, and therefore emissions.
TGS also successfully tested 100% HVO (Hydrotreated vegetable oil, a biofuel) on a T-class vessel. The test used HVO with WtW emissions of 4,2 gCO2eq/MJ, compared to VLSFO’s 91,6 gCO2eq/MJ. This means TGS has the potential to deploy this fuel system to its other T-class engines within the TGS vessel fleet and/or provide a dual fuel option, should clients require it.
 Finally, TGS continues to explore other initiatives to improve vessel operational efficiency, including using adjustable deflectors on streamers that will allow vessels to take turns more efficiently, testing the feasibility of changing to smaller rope diameters for towing equipment to reduce drag and improve fuel efficiency, and testing a Technotherm storage device to store waste heat and convert it to energy for use on offshore operations.
Finally, TGS continues to explore other initiatives to improve vessel operational efficiency, including using adjustable deflectors on streamers that will allow vessels to take turns more efficiently, testing the feasibility of changing to smaller rope diameters for towing equipment to reduce drag and improve fuel efficiency, and testing a Technotherm storage device to store waste heat and convert it to energy for use on offshore operations.
Can TGS give a specific example of having a positive impact on biodiversity?
TGS is an active contributor and supporter of the Sustainable Seas Initiative. As part of this initiative, TGS actively picks up, and requires any contract vessel providers to pick up, any discarded fishing gear or other marine debris they come across during marine operations, ensuring that it is properly disposed of and does not cause issues to marine life. In October 2024, during one of its operations, the TGS crew spotted a turtle trapped inside a net near floating fishing buoys. The team in the workboat crew found a way to gently remove the debris and free the turtle. This year, TGS marine operations removed over 47 tonnes of discarded fishing gear and marine debris.
 Can TGS give a specific example of using the Circular Economy framework?
Can TGS give a specific example of using the Circular Economy framework?
TGS underwent several office relocations. The management teams focused on repurposing, reusing, or recycling where possible. This meant utilizing good quality furniture, air-conditioning, and IT equipment between TGS sites globally to reduce waste. Where items were not needed but still had life in them, TGS used recycling or donation programs benefiting local schools or charities. Where possible, TGS will also try to donate or repurpose PPE gear to benefit local programs. As an example, TGS recently donated a surplus of Crewsaver life jackets to an Istanbul-based search and rescue group.
What is the future of TGS’ ESG initiatives?
TGS is committed to continuously enhancing its current ESG initiatives while exploring additional sustainable solutions for the environment and its workforce. TGS’ workforce is encouraged to innovate and propose improvements in pursuit of this goal, and the company is actively seeking external opportunities or partnerships to improve and expand on existing Sustainability initiatives.
TGS also believes in transparently reporting its strategy and progress so that its key stakeholders understand the company’s objectives. TGS’ 2024 Sustainability Report, which will be published later this year, will align with the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and related European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS), which are intended to enable consistent Environmental Social Governance (ESG) reporting while increasing global reporting transparency. TGS will also continue to be an active supporter of the UN Global Compact and its 17 Sustainable Development Goals.
 Valaris has made significant strides in 2024, showcasing its commitment to innovative technologies, best practices, and initiatives that emphasize environmental protection and stewardship, social responsibility, and governance excellence. The following highlights some of the key achievements and initiatives that Valaris has undertaken in these areas.
Valaris has made significant strides in 2024, showcasing its commitment to innovative technologies, best practices, and initiatives that emphasize environmental protection and stewardship, social responsibility, and governance excellence. The following highlights some of the key achievements and initiatives that Valaris has undertaken in these areas.
Environmental Protection and Stewardship
Valaris has consistently demonstrated its dedication to environmental protection through various innovative technologies and practices. One of the notable initiatives in 2024 is the implementation of rig engine optimization projects aimed at reducing emissions. These projects have been instrumental in minimizing the environmental impact of Valaris' operations by optimizing the performance of rig engines to reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
For its drillships, Valaris accomplishes this through the operation in two diesel generator mode (2DG) and the ABS Enhanced Electrical System notation (EHS-E) on the DS-7, DS-12, and DS-17. The ABS EHS-E notation recognizes sophisticated system designs that enhance reliability and protection, allowing these drillships to optimize the powerplant output by operating on fewer generators, thereby reducing fuel consumption and emissions. The 2DG operation mode involves running two diesel generators instead of the traditional three or more, improving fuel efficiency.
These three drillships achieved an average of 10% in fuel savings compared to their pre-upgrade consumption. Valaris intends to implement this upgrade on more drillships in the future, further underscoring their dedication to sustainable practices and setting new benchmarks in operational efficiency and environmental compliance within the industry.
For its jackups, Valaris developed an in-house advisory tool, the Engine Optimization Dashboard, to analyze engine loads. This tool provides an instant overview of power usage and recommendations for starting or stopping extra engines based on the on-going operation. Following these recommendations led to 5% fuel-savings and will reduce maintenance due to fewer engine hours.
Social Responsibility
Valaris' commitment to social responsibility is evident in its various initiatives aimed at supporting local communities and promoting employee well-being. In 2024, Valaris continued to support the health and well-being of its crews and business partners through several initiatives. These include providing medical care to employees, sharing health and wellness tips on our employee engagement platform, and offering medical fitness checks and immunizations for the local workforce.
Valaris also promotes inclusive and equitable quality education by offering technical and health, safety, and environment (HSE) training in several languages for offshore crews. The company supports continuing professional development for both onshore and offshore personnel and offers internships for graduates to prepare them for future employment opportunities.
A significant highlight in 2024 is Valaris' new hire training rig program. This program is designed to prepare and equip new employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their duties safely and effectively. The program includes a comprehensive orientation that covers various aspects of rig operations, safety protocols, and company policies. New hires undergo a rigorous training schedule that includes facility induction, personal protective equipment issuance, rig tours, and detailed training on industry-specific topics. This initiative not only enhances the competency of new employees but also reinforces Valaris' commitment to maintaining its safety and operational standards.
In 2024, Valaris also rolled out Starlink services to improve bandwidth on its rigs. This initiative has significantly enhanced communication capabilities, allowing for better connectivity and data transfer. The improved bandwidth has facilitated more efficient operations, enabling real-time data sharing and remote monitoring. This technological advancement has not only improved operational efficiency but also enhanced the overall well-being of the crew by providing reliable communication channels.
In terms of economic support, Valaris has made contributions to local economies by providing job opportunities, offering training programs to enhance skills and capabilities, and sourcing goods and services locally where practicable. These efforts not only support local economies but also promote sustainable development.
Governance Excellence
Valaris has established a robust governance framework that promotes ethical business practices and compliance with regulatory requirements. The company's governance policies and Code of Conduct cover a wide range of areas, including ethics, conflicts of interest, anti-bribery, trade compliance, human rights, and cybersecurity.
Valaris also places a strong emphasis on transparency and accountability. The company reports its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, including Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions, in its annual sustainability reports in line with SASB and TCFD framework guidelines. This transparency allows stakeholders to assess Valaris' environmental impact and track its progress in reducing emissions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Valaris has made significant progress in 2024 in the areas of environmental protection and stewardship, social responsibility, and governance excellence. The company's innovative technologies, best practices, and initiatives demonstrate its commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices. By continuing to prioritize these areas, Valaris is well-positioned to lead the industry in promoting a sustainable and responsible future.

 NOIA’s work in ESG includes supporting offshore energy education for teachers and students. For over 25 years we have worked with the National Energy Education Development (NEED) Project to provide energy training and offshore energy curriculum to schools. Central to our work is the annual Offshore Energy Workshop hosted at the NOIA Fall Meeting each year. This workshop brings together up to 50 local educators to dive into hands-on exploration of offshore energy exploration, production, and use. Several NOIA Members take time to speak to the teachers about their company’s services, technologies, and career opportunities.
NOIA’s work in ESG includes supporting offshore energy education for teachers and students. For over 25 years we have worked with the National Energy Education Development (NEED) Project to provide energy training and offshore energy curriculum to schools. Central to our work is the annual Offshore Energy Workshop hosted at the NOIA Fall Meeting each year. This workshop brings together up to 50 local educators to dive into hands-on exploration of offshore energy exploration, production, and use. Several NOIA Members take time to speak to the teachers about their company’s services, technologies, and career opportunities.
NEED programs are designed to meet partner needs for workforce development and community engagement while also meeting the STEM needs of the classroom. Bringing together the energy industry and the classroom provides an opportunity for students, teachers, and families to better understand the energy we use today and will use tomorrow. Some of NEED’s STEM programs include week-long summer experiences for high school students, particularly young women. These experiences provide students the opportunity to engage with energy industry professionals, tour energy industry facilities, and to work on a solution to an energy challenge with a small team. Participating students build energy knowledge, life skills, and valuable work skills that will serve them well in trade school or college and beyond into their careers.
NEED celebrates its 45th year in 2025 and continues to grow – adding more teacher and student workshops, new curriculum modules, new workforce and student engagement programs each year. NEED by the numbers tells the story of an organization doing impactful work for teachers and students with the support of the energy industry nationwide.
In 2024:
- 136 sponsored one day energy workshops for educators
- Attended by 3,021 educators from 1,885 schools across 932 cities, 35 states, and Washington, D.C.
- At least 585,919 students expected to be reached utilizing materials and curriculum presented at the workshop
- Energy pre and post tests given at each workshop, with an average knowledge posttest increase of 93%
- 99% of participating educators would recommend NEED materials to other teachers
- Majority (70%) of workshop participants had never attended a prior energy training program before
- NEED was present with hands-on sessions and exhibits at 27 science and environmental conferences and conventions across the United States
- NEED summer student programs reached 806 students in summer camps, weeklong STEM Academies, and workforce skills trainings.
NOIA members and partners supporting NEED programming in their local communities include:
- BP
- ConocoPhillips
- Offshore Technology Conference
- Shell
- Society of Petroleum Engineers
- Vineyard Wind
- Williams
To learn more about NEED, visit www.need.org and plan to attend the NOIA Fall Meeting and stop in to see the Offshore Energy Workshop in action.

